In today’s world, the construction sector is facing numerous challenges that threaten the sustainability of the industry. One major issue is the depletion of natural sand, which is rapidly becoming a scarce resource. Experts predict that we might completely run out of natural sand by the year 2050. In addition to the sand scarcity problem, carbon dioxide emissions from processes like cement manufacturing and fired clay bricks production are on the rise. These emissions contribute significantly to the worsening global climate crisis. Furthermore, the generation of construction and demolition (C&D) waste is increasing, with about 150 million tons being produced annually in India alone. Despite the high volume of C&D waste generated, the recycling rate remains dismally low at only about 1%.
To address these pressing challenges, researchers at the Center for Sustainable Technologies (CST) at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) are pioneering innovative solutions. One of the key areas of focus for the researchers is exploring ways to capture carbon dioxide from industrial flue gas and store it in excavated soil and C&D waste. By utilizing these materials as substitutes for natural sand in construction, the environmental impact of building materials can be significantly reduced. Moreover, these carbon dioxide-treated materials can possess enhanced properties that make them suitable for construction applications.
Impact on Construction Materials
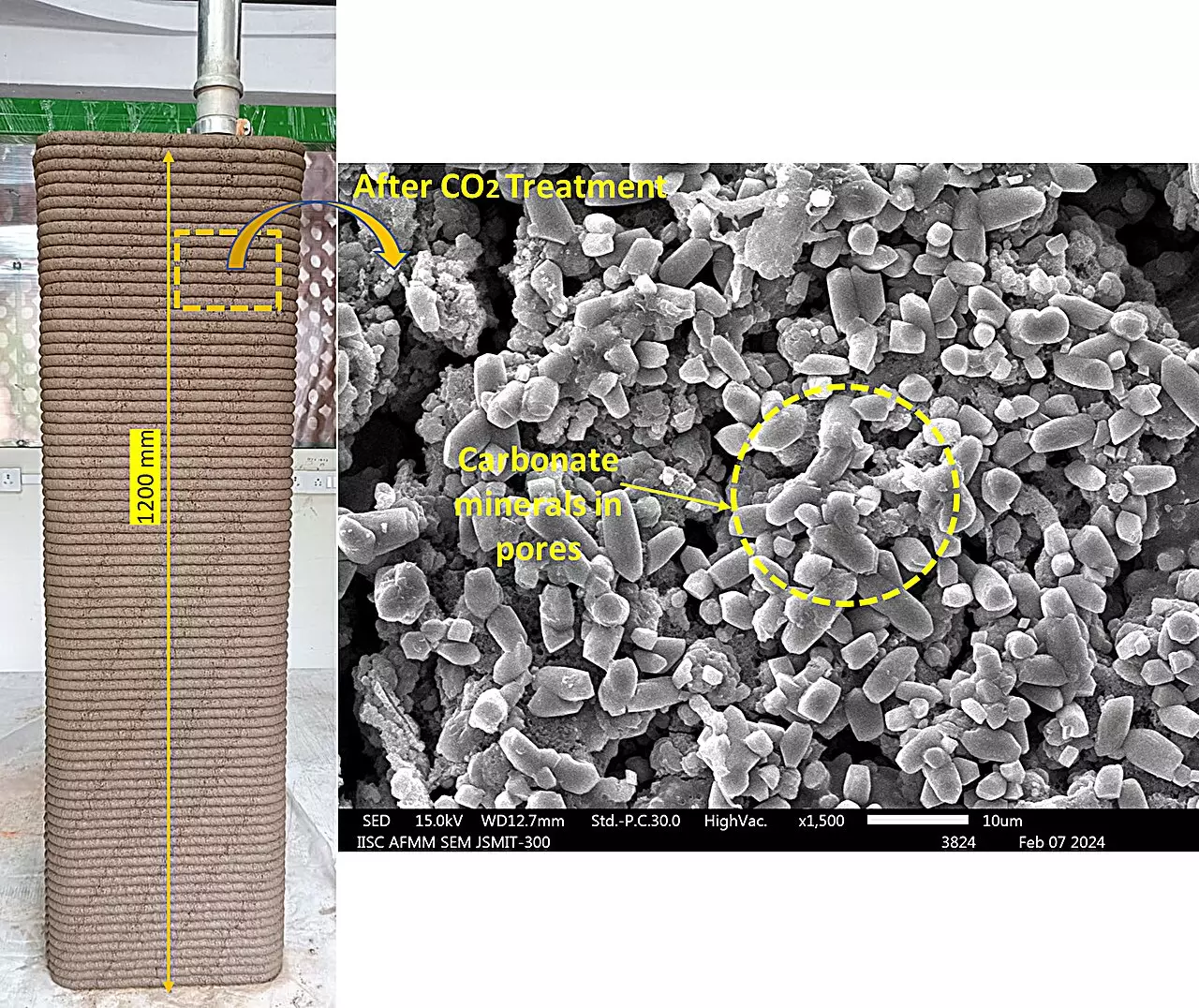
Studies conducted by the team at CST have shown promising results in the utilization of carbon dioxide-treated C&D waste in mortar. By replacing natural sand with these treated materials and curing them in a CO2-rich environment, the engineering properties of the material can be accelerated. The compressive strength of the mortar was found to increase by an impressive 20-22% through this process. Additionally, injecting carbon dioxide gas into clayey soil has led to improved stabilization of clay, reduced surface area, pore volume, and enhanced bulk engineering performance. These findings were published in reputable journals like Construction and Building Materials and Developments in the Built Environment.
In a recent study published in Science of The Total Environment, Gupta’s team investigated the impact of sequestering carbon dioxide in excavated soil to develop cement-lime-soil materials. These materials were then used to replace a significant portion of fine aggregates in mortar, resulting in improved compressive strength. Furthermore, the team has developed 3D-printable materials using excavated soil stabilized with binders like Portland cement, blast furnace slag, and fly ash. These materials exhibit superior extrusion and buildability characteristics compared to conventional cement-sand mortars, and they require significantly less cement and natural sand. This innovation has the potential to reduce the environmental footprint of construction projects.
Moving forward, the research team plans to explore the effects of industrial and simulated flue gas on the properties of the newly formulated materials. By understanding how different gases impact carbon sequestration and engineering properties, they aim to optimize the performance of sustainable construction materials. The team is also in discussions with major construction companies to implement these innovations in their manufacturing processes. Additionally, Gupta is actively involved in revising industry standards for natural and recycled aggregates in cement-based construction materials to promote sustainable practices and reduce the climate change impacts of the construction industry.
The future of sustainable construction lies in innovative approaches to carbon sequestration and the utilization of alternative materials. By tackling the challenges of sand scarcity, carbon emissions, and waste generation through research and technological advancements, the construction sector can move towards a more environmentally-friendly and resilient future. Collaborative efforts between researchers, industry partners, and regulatory bodies are essential to driving these changes and creating a greener construction industry for generations to come.