The recent study conducted by researchers in Japan sheds light on the transmission of quantum information within interacting boson systems, particularly Bose-Einstein condensates (BECs). The Lieb-Robinson bound, governing the speed at which information propagates through quantum many-body systems, has long posed a challenge in understanding systems with interacting bosons. This study, led by Dr. Tomotaka Kuwahara, aims to address this challenge and provide valuable insights into the dynamics of boson systems.
The Lieb-Robinson bound establishes a universal speed limit on how quickly correlations or influences can spread between different regions of a quantum system. Inspired by Einstein’s theory of relativity, this bound creates a framework for understanding the propagation of information in quantum systems. In the case of interacting boson systems, the complexities arise from unbounded energy limits and long-range interactions among bosons, making it difficult to develop accurate theoretical models and simulations.
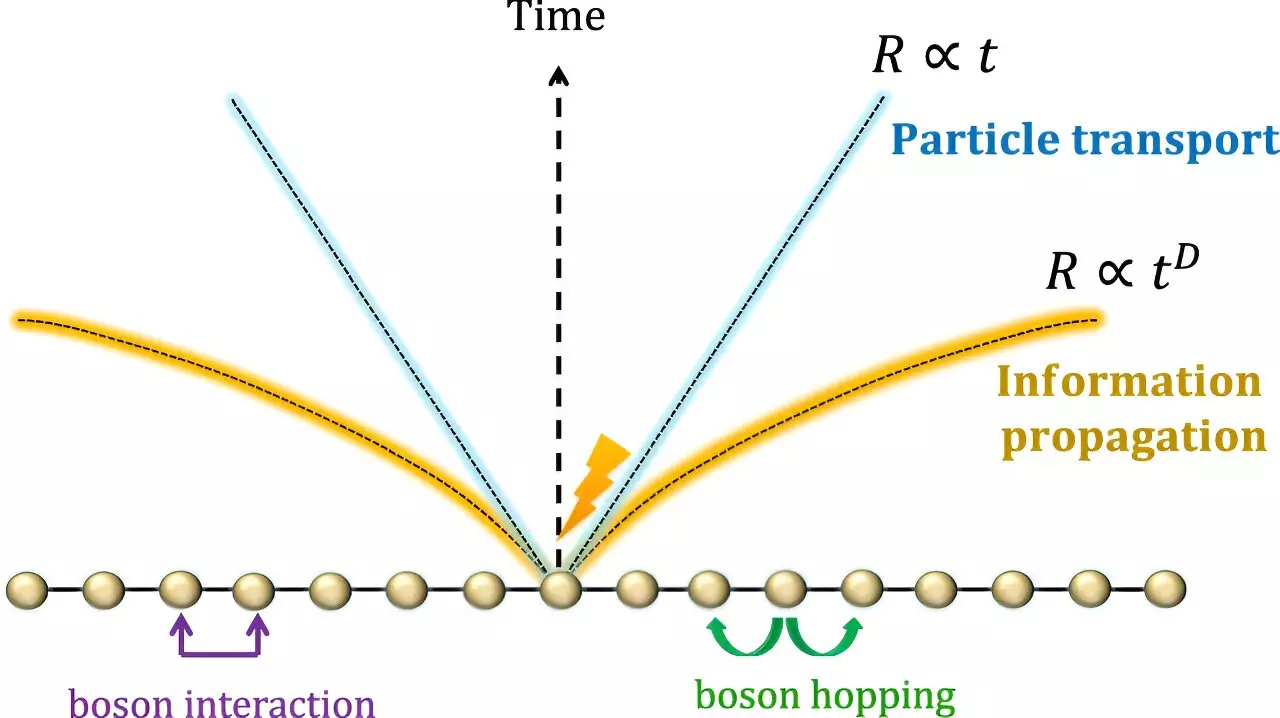
The researchers utilized the Bose-Hubbard model to investigate the Lieb-Robinson bounds in interacting boson systems. This theoretical framework considers factors such as boson hopping between lattice sites and on-site repulsive interactions. By studying a D-dimensional lattice system governed by the Bose-Hubbard model, the researchers identified key results that shed light on the dynamics of boson transport within the system.
One crucial finding from the study is the limitation on the speed of boson transport, even in systems with long-range interactions. The speed of information propagation grows at most logarithmically with time, indicating a relatively slow rate of transmission within interacting boson systems. This observation provides valuable insights into the upper bounds of information propagation in such systems.
The study also explores error propagation in interacting boson systems, highlighting the accumulation of error as operators deviate from the ideal evolution. Despite the presence of an upper bound on error propagation, interactions among bosons lead to clustering in specific regions, facilitating accelerated information propagation along certain lattice paths. This clustering effect influences the rate of information transmission within the system.
The study contrasts the speed of information propagation in bosonic systems with fermionic systems, revealing that bosons can transmit information faster, especially as more bosons cooperate. The non-linear nature of information propagation in bosonic systems allows for accelerated transmission over time, challenging previous assumptions about the speed limits in quantum systems.
Dr. Kuwahara anticipates that the findings from this study will pave the way for simulating condensed matter physics and exploring new quantum phases in interacting boson systems. The algorithm developed by the researchers holds promise for simulating quantum thermalization and understanding the dynamics of closed quantum systems over time. This work opens up new possibilities for investigating quantum information propagation and its implications for various branches of physics.
Overall, the study provides a critical analysis of the propagation of quantum information in interacting boson systems, offering valuable insights into the dynamics of these complex quantum systems. Through the exploration of the Lieb-Robinson bound and the Bose-Hubbard model, the researchers have advanced our understanding of information transmission within quantum many-body systems. This research sets the stage for future investigations into the behavior of interacting boson systems and their potential applications in quantum physics.