Photonic quantum computers have shown great promise in the realm of quantum computing due to their utilization of particles of light as information processing units. However, the weak interactions between individual photons have hindered the progress of photonic quantum computers in achieving desired results. Recent research by the University of Science and Technology of China has shed light on a new approach that could facilitate quantum computation in photonic systems, particularly through the demonstration of three-photon entanglement.
The key challenge in photonic quantum computing lies in the weak interaction between single photons, which is essential for the realization of deterministic two-qubit gates necessary for scalability. To address this issue, researchers have explored the concepts of fusion and percolation as scalable approaches to quantum computation in photonic systems without the need for deterministic entangling gates. By fusing small resource states into large-scale cluster states, researchers have laid the groundwork for measurement-based quantum computing in the photonic domain.
Through the use of a strategy involving the generation of the necessary resource state followed by the fusion of small states into large-scale entangled states, researchers have successfully demonstrated the heralded 3-GHZ state in a photonic system. This achievement represents a significant milestone towards realizing fault-tolerant photonic quantum computing. By harnessing the power of heralded single photons and entangled clusters, researchers have made strides towards the development of large-scale optical quantum computers that rely on 3-GHZ states for processing quantum information.
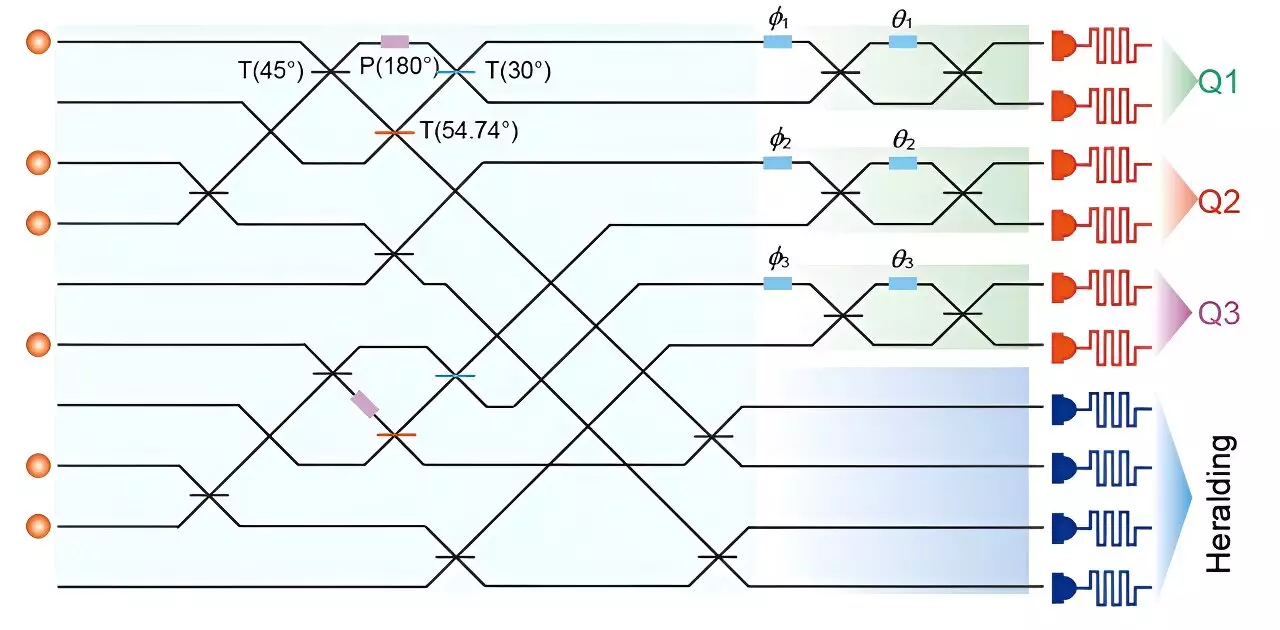
The experimental setup utilized by the researchers involved injecting six single photons into a 10-mode passive interferometer, with the single-photon source being an InAs/GaAs quantum dot. The programmable interferometer, which demonstrated an overall efficiency of 50%, played a crucial role in generating the heralded 3-GHZ state. Through the application of specific unitary transformations, the researchers were able to encode the output state across multiple ports, leading to the successful creation of the 3-GHZ state.
The recent advancements in photonic quantum computing, particularly the successful demonstration of the heralded 3-GHZ state, pave the way for further research and development in the field. With the possibility of achieving a demonstration of a fusion gate surpassing the percolation threshold using eight single photons in the foreseeable future, researchers are optimistic about the potential for building upon the success of the current study. The ability to amalgamate multiple 3-GHZ resource states to form a more extensive entangled state represents a promising avenue for future exploration in the realm of fault-tolerant photonic quantum computing.
The breakthroughs in photonic quantum computing, as demonstrated by the research conducted by the University of Science and Technology of China, hold significant implications for the future of quantum computing. By leveraging the power of three-photon entanglement and large cluster states, researchers are paving the way for the development of robust and scalable photonic quantum computers. With further advancements and collaborations within the scientific community, the realization of fault-tolerant photonic quantum computers may be closer than we think.