The development of robots for maintenance tasks has been an area of great interest for engineers and researchers. The use of robots in infrastructure maintenance has shown great potential, but one of the main limitations has been the need for external power sources. However, a recent breakthrough by researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, Harbin Institute of Technology, and Hong Kong University of Science and Technology has led to the creation of a new wireless miniature robot that can navigate through pipes and other structures without external power sources.
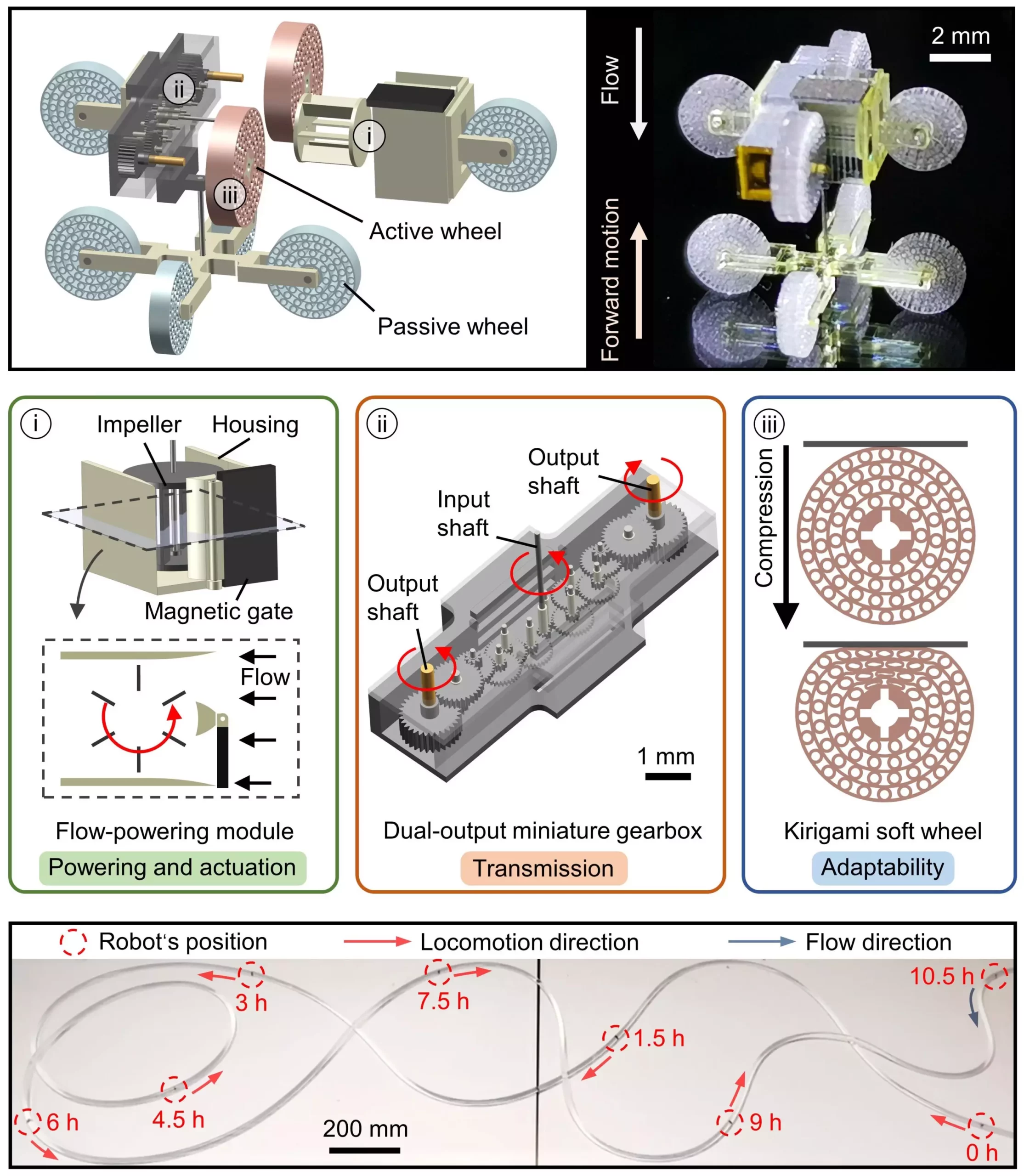
The newly developed wireless millimeter-scale robot includes an internal power source and an actuation unit, allowing it to cover longer distances within tubular structures and perform maintenance tasks for prolonged periods without running out of energy. This robot incorporates a flow-powering module, a dual-output miniature gearbox, and kirigami soft wheels for adaptive locomotion in complex tubes. The ability of the robot to convert fluid flow into mechanical energy and modulate its direction with an external magnetic field makes it suitable for a variety of applications.
The researchers conducted preliminary tests on the robot and found that it achieved promising results. The robot was able to navigate through complex pipelines and perform tasks within confined tubular structures filled with flowing gases or liquids. However, there is still room for improvement in terms of the robot’s capabilities and stability. One of the challenges that the researchers are looking to address in future studies is the anchoring force needed to balance flow resistance on the robot’s body, especially in high-flow rate environments.
Future Enhancements
To ensure stable locomotion in tubes with high flow rates or low-friction surfaces, the researchers are considering streamlining the robot body to minimize flow resistance or adding microstructures to the wheel surfaces to increase friction. Additionally, the limitation of the robot’s motion status switching due to the working distance of external magnetic fields is another area of focus for future enhancements. By addressing these challenges and optimizing the robot’s design, the researchers hope to facilitate its future deployment in real-world settings.
The development of wireless miniature robots for maintenance tasks represents a significant breakthrough in the field of robotics. The ability of these robots to navigate through tubular structures without external power sources opens up new possibilities for inspection, maintenance, and repair applications in various industries. With further research and enhancements, these robots could revolutionize maintenance tasks and minimize damage to infrastructure. The potential of wireless miniature robots for maintenance tasks is truly promising, and the collaboration between researchers from different institutions has paved the way for future developments in this area.