The clash between sustainable energy practices and traditional agricultural methods is a prominent issue in today’s world. This is evident in cultural representations and ongoing research initiatives. The emergence of agrivoltaics, which involves combining agricultural and photovoltaic production on the same land, is seen as a potential solution to this conflict.
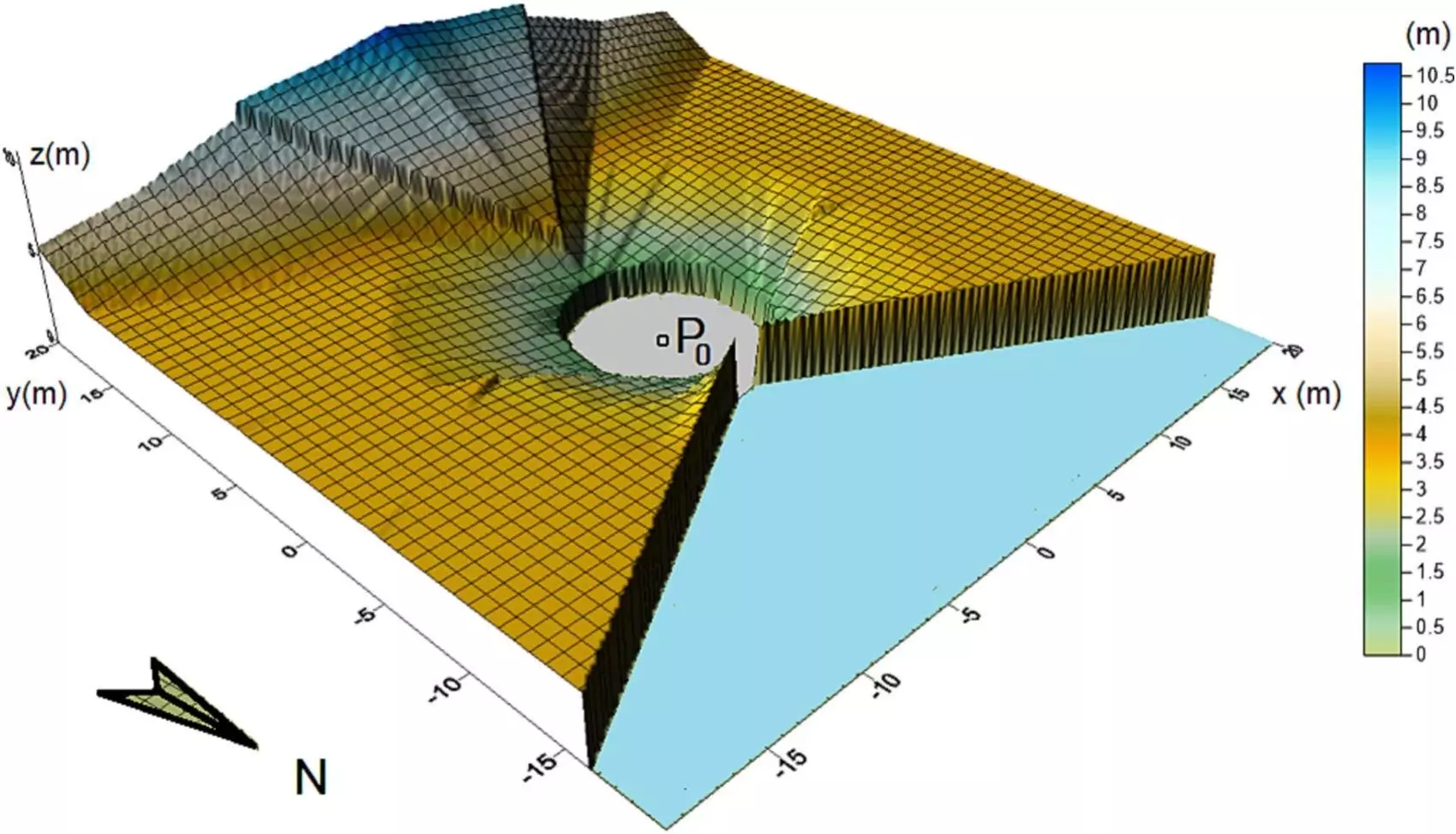
Recently, the TEP215-Physics for Renewable Energies research group at the University of Cordoba created a groundbreaking methodology. This model specifically focuses on identifying the cultivable space between two-axis photovoltaic modules. The objective behind this initiative is to encourage the transformation of existing photovoltaic plants into agrivoltaic systems.
The research takes into account the movement patterns of two-axis solar panels, which mimic the sunflower’s ability to track the sun. By analyzing the spatial geometry and solar astronomy of a photovoltaic plant, the model outlines areas where agricultural crops can be grown without impeding the panels’ movement or reducing energy production.
Utilizing an actual photovoltaic installation in Cordoba known as “El Molino,” the researchers discovered that 74% of the land between panels is suitable for growing crops under 1.4 meters in height. This finding indicates the potential for maximizing land use efficiency and transitioning towards agrivoltaic practices.
The integration of agriculture and solar energy production not only increases overall productivity but also contributes to environmental sustainability. Through shading from solar panels, crops can benefit from extended soil moisture retention, particularly in regions with extreme climates.
The development of legislation surrounding agrivoltaics and conducting field trials with various crop types are crucial next steps towards widespread implementation. This would further solidify the potential benefits of agrivoltaic systems and advance efforts in combating climate change.
This innovative approach represents a significant leap forward in advancing agrivoltaic practices and enhancing the sustainability of large-scale photovoltaic plants. By bridging the gap between traditional agriculture and renewable energy production, the future of agrivoltaics holds promise for a more harmonious coexistence between these two vital sectors.