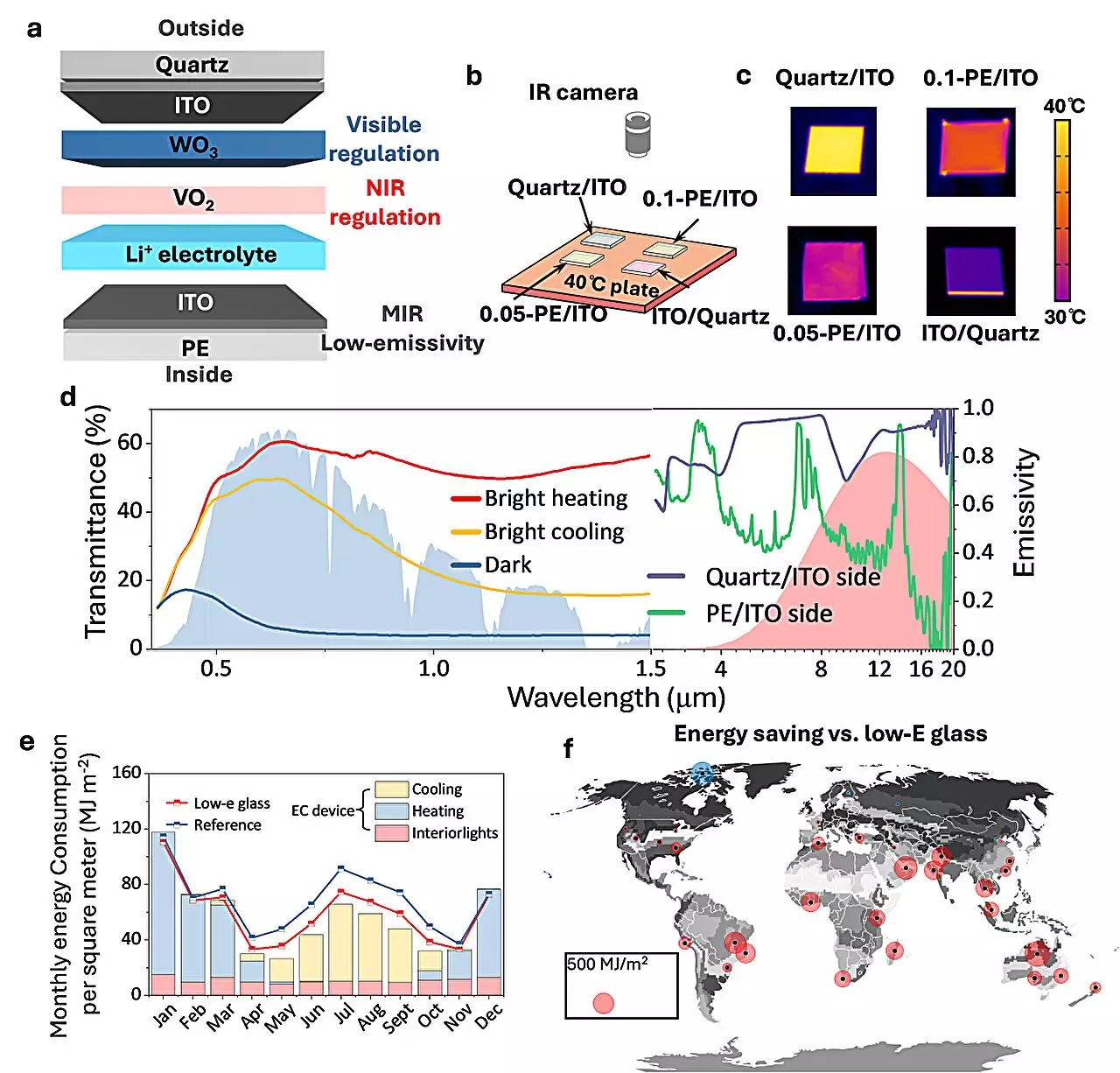
In a groundbreaking study published in Nature Sustainability, a research team led by Prof. Cao Xun from the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has revolutionized the field of energy-saving windows. Electrochromic smart windows, which have the ability to dynamically regulate solar radiation under external voltage stimuli, have long been touted as a promising technology for reducing the energy consumption of buildings. While previous efforts have focused on improving response speed and contrast ratio, little progress has been made in addressing the influence of solar radiation and outdoor temperature.
To address these challenges, the researchers designed a new electrochromic smart window system based on a VO2-WO3 tandem film via a solid electrolyte. This cutting-edge technology allows for the tri-stable control of solar heat and sunlight transmittance simultaneously, resulting in significant energy savings. By leveraging the unique properties of VO2 and WO3, the system enables independent regulation of near-infrared (NIR) and visible transmittance of sunlight. Notably, the use of VO2 ensures non-volatility by decoupling the barrier for maintaining the state from the barrier for changing the state, setting it apart from traditional materials like WO3.
Optimizing Energy Efficiency
One of the key advantages of this new electrochromic smart window system is its ability to minimize the total energy cost of indoor lighting and heat exchange. By strategically controlling the transmission of sunlight, the windows offer unparalleled energy savings compared to conventional low-E glass. Simulations have demonstrated superior heating and cooling energy savings across a wide range of climates worldwide, making this technology a game-changer in the realm of energy-efficient building design.
Outdoor experiments conducted in Sanya, Hainan Province and Shanghai have further validated the effectiveness of this innovative smart window technology. In a typical clear sunny day scenario, the electrochromic windows were able to achieve continuous cooling of up to 2°C–14°C throughout the day. This real-world data underscores the practical application and immense potential of these energy-saving windows in reducing the environmental impact of buildings while enhancing occupant comfort and energy efficiency.
The development of this new electrochromic smart window system marks a significant advancement in the quest for sustainable building technologies. By leveraging cutting-edge materials and innovative design principles, researchers have unlocked a new era of energy-saving windows that promise to reshape the way we think about building efficiency and environmental sustainability.