Metal halide perovskites are a unique class of crystalline materials that have shown remarkable optoelectronic properties, making them ideal candidates for thin-film transistors. While tin (Sn) halide perovskites have been successfully used to fabricate high-performing p-type transistors, the development of n-type transistors using these materials has been challenging due to their poor suitability for such applications. This limitation has hindered the creation of complementary logic circuits that require both p-type and n-type transistors with similar performance levels.
New Strategies for N-type Transistors
To address this gap in the literature, researchers from the National Centre for Scientific Research Demokritos, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), the Indian Institute of Technology, and other institutes worldwide have introduced a new strategy for developing metal halide perovskite-based n-type transistors. In a recent paper published in Nature Electronics, they detailed a method that enabled them to fabricate n-type transistors with field-effect mobilities of up to 33 cm2 V−1 s−1 using formamidinium lead iodide (FAPbI3) perovskite.
One key aspect of the research involved the use of a methylammonium chloride (MACI) additive to enhance the performance of the n-type transistors. This additive helped regulate the strain in FAPbI3, improving its properties and overall functionality. By leveraging strain relaxation of the perovskite lattice and minimizing undercoordinated lead through tetramethylammonium fluoride multidentate anchoring, the researchers were able to stabilize the alpha phase, achieve a balance in strain, and enhance surface morphology, crystallinity, and orientation.
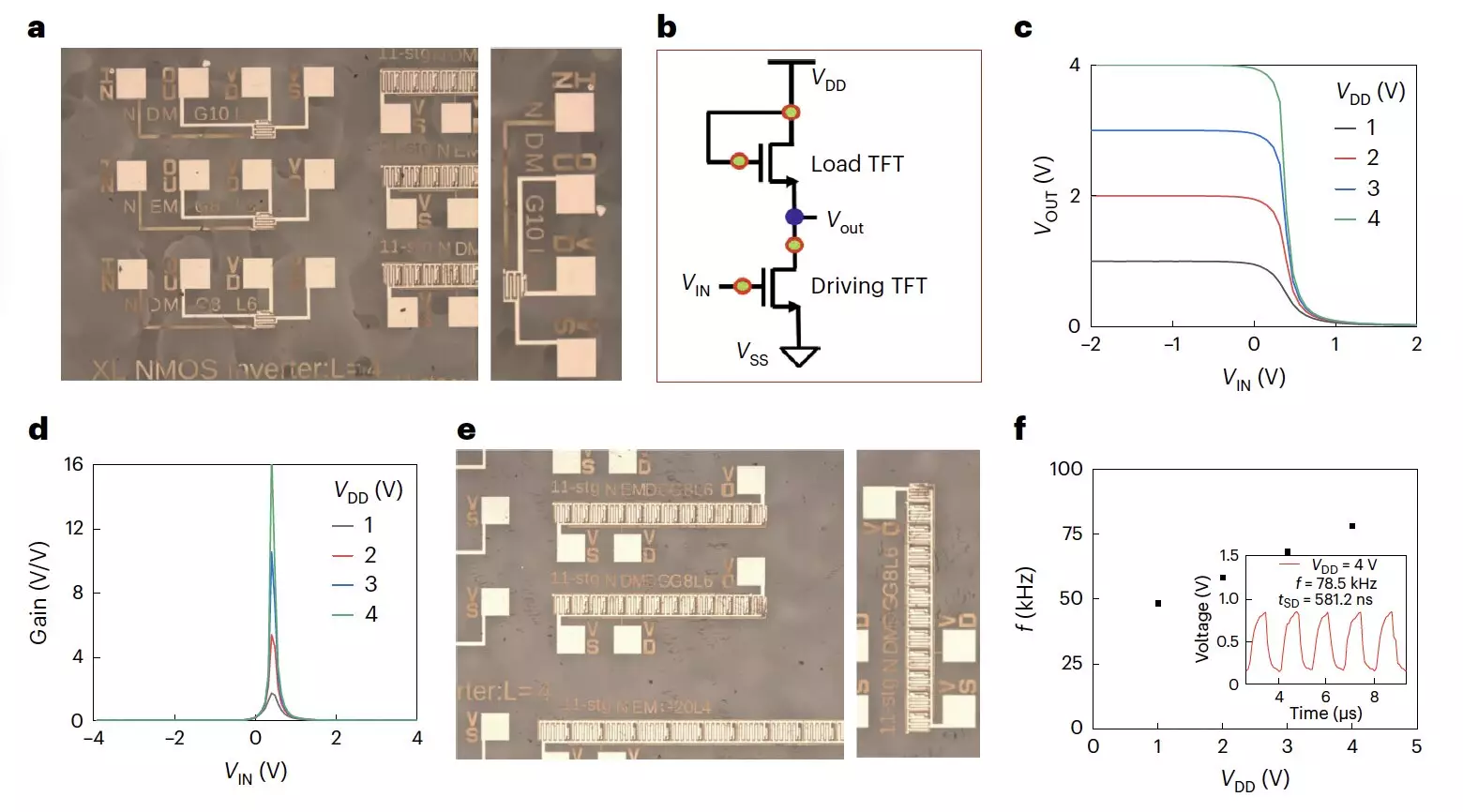
Initial tests conducted on the n-type transistors yielded promising results, including good electron mobilities, minimal hysteresis, and high operational stability under both negative and positive bias stress. The researchers further utilized these transistors to create all-perovskite unipolar inverters and 11-stage ring oscillators, demonstrating the potential for integrating metal halide perovskite transistors into various electronic components. This innovative fabrication strategy opens up new possibilities for highly performing and cost-effective integrated circuits containing metal halide perovskite transistors.
Future Directions
Moving forward, the researchers plan to continue testing and refining their n-type transistors for integration into a wide range of electronic applications. By exploring the potential of metal halide perovskites further, there is a significant opportunity to advance the field of thin-film transistors and pave the way for the development of next-generation integrated circuits with superior performance characteristics. The continued evolution of metal halide perovskite-based transistors holds promise for revolutionizing the electronics industry.