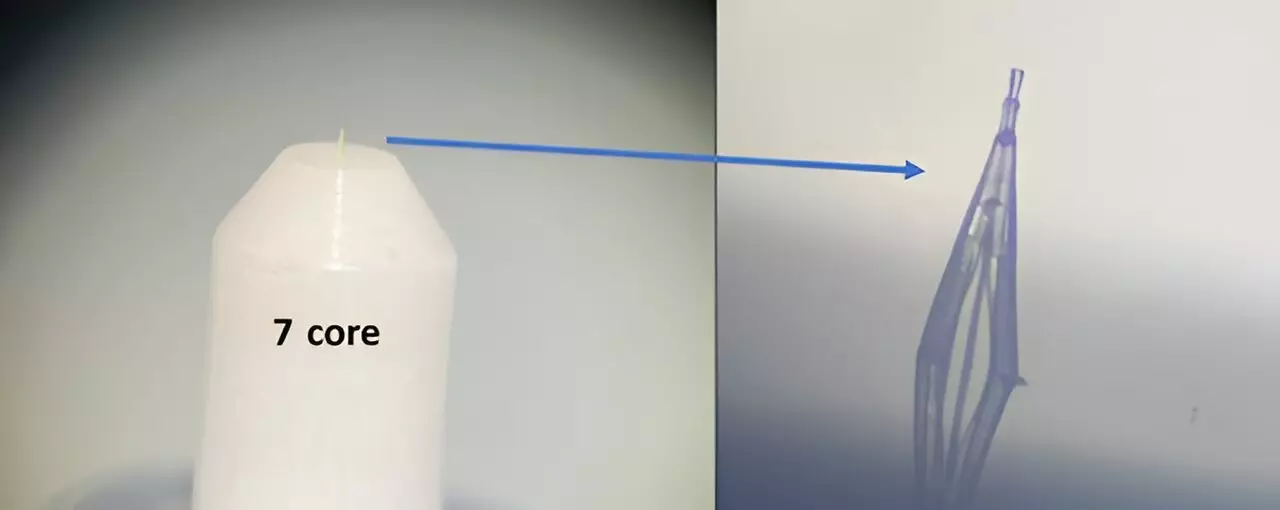
The field of optical technology has seen significant advancements in recent years, particularly in the realm of spatial mode manipulation. This has led to the development of compact and versatile devices that have the potential to revolutionize imaging, communication, and directed energy applications. One such advancement is the creation of free-standing microscale photonic lantern spatial mode (de-)multiplexers using 3D nanoprinting techniques.
The recent study on the development of microscale photonic lanterns marks a major milestone in the field of photonic technology. These devices are characterized by their compactness, minimal footprint, and ability to directly print on various optical components, making them highly versatile and adaptable for a wide range of applications. The integration of these devices into high-capacity communication systems and demanding imaging modalities holds immense promise for the future.
Key Findings
Ph.D. candidate student Yoav Dana, along with Professor Dan Marom and their team at the Institute of Applied Physics, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, in collaboration with scientists from Nokia Bell Labs, have successfully developed and demonstrated a free-standing microscale photonic lantern spatial mode (de-)multiplexer. This device, fabricated using 3D nanoprinting techniques, offers a compact and efficient solution for converting optical waves containing a superposition of modes into single-mode signals.
By harnessing the capabilities of 3D nano-printing and utilizing high-index contrast waveguides, the researchers have created a device that can be printed onto nearly any solid platform with exceptional accuracy and fidelity. This level of precision enables seamless integration into a variety of technological contexts, opening up new possibilities for optical communication, imaging, and other spatial manipulation applications.
The development of free-standing microscale photonic lanterns represents a significant advancement in enabling and adopting spatial multiplexing for diverse optical systems. This breakthrough makes space division multiplexing technology more accessible and amenable towards integration, paving the way for enhanced optical communication and imaging applications. The compact size of these devices, coupled with their impressive performance metrics, makes them a promising solution for next-generation optical technologies.
The emergence of free-standing microscale photonic lanterns through 3D nanoprinting techniques represents a major leap forward in spatial mode manipulation. These devices offer a compact, versatile, and highly efficient solution for converting optical wavefronts and enabling space division multiplexing in various applications. The research conducted by Dana, Marom, and their team sets the stage for further advancements in optical technology and holds great promise for the future of high-capacity communication systems and advanced imaging modalities.