The demand for wireless internet access continues to grow, supporting various activities ranging from professional communications to entertainment. With this surge in demand comes an increase in power consumption, leading to a rise in carbon emissions globally. In order to address the need for efficient wireless networks that can support modern applications and services while minimizing energy usage, researchers have been exploring innovative solutions.
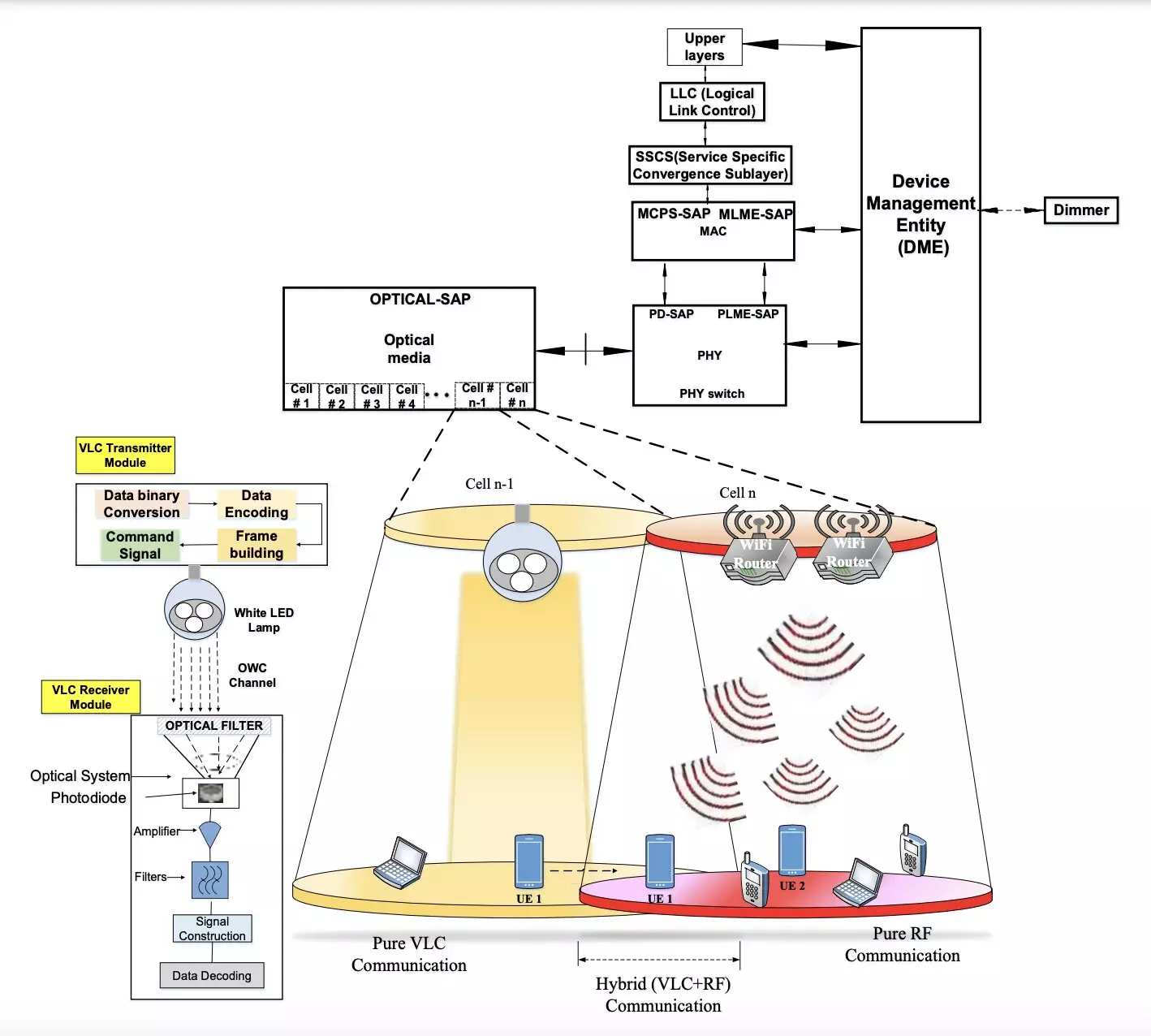
One such solution gaining traction is visible light communication (VLC), which utilizes visible light to transmit data through light-emitting diodes (LEDs) or other artificial light sources. Researchers at Central University (CU), IIDM, and CU J&K in India have recently introduced a hybrid approach that combines VLC with RF communication. This hybrid solution, as detailed in a paper published in IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, aims to enable reliable communication in indoor environments with high data transmission rates while consuming less energy.
The wireless communication system developed by the research team consists of two main components: a transmitter and a receiver module. These modules are physically separated but connected through a VLC channel. The transmitter utilizes LEDs to transmit binary data in the form of light, while the receiver, equipped with a photo-sensitive device such as a photodiode or camera, extracts the transmitted information from the light emitted. By employing modulation schemes and continuous data streams, the system maintains a constant power consumption level throughout communication.
The researchers conducted an initial evaluation of their wireless communication system using simulation platforms such as Python, Scilab, and MathWorks tool. The results indicated that the proposed system enables stable communication within indoor environments, delivering substantial energy savings. The comparative analysis conducted for RF communication, hybrid (RF + VLC), and pure VLC demonstrated high energy efficiency, low Specific Absorption Rate (SAR), and decreased power density in human tissues exposed to radiation. Additionally, the system increased the battery lifetime of mobile devices by approximately 7 hours, showcasing its potential for practical application.
This study by the research team contributes to ongoing efforts aimed at reducing power consumption and electromagnetic radiation in wireless communications. The promising results from the initial simulations suggest that the proposed hybrid approach has the potential to enhance energy efficiency and optimize communication systems. Further research and testing will be crucial in refining and validating the effectiveness of this innovative wireless communication solution.
The future of wireless communication lies in energy-efficient techniques that prioritize sustainability and user experience. The integration of VLC and RF communication in indoor environments represents a significant step towards achieving reliable, low-energy consumption wireless networks. By continuing to innovate and explore new technologies, researchers can pave the way for a more sustainable and efficient wireless communication landscape.