Recently, the introduction of quantum networks into the market has been a significant challenge for engineers due to the fragility of entangled states in a fiber cable and the efficiency of signal delivery. However, a team of scientists at Qunnect Inc. in Brooklyn, New York, have made groundbreaking progress by successfully operating a quantum network under the bustling streets of New York City. This achievement marks a significant step towards establishing stable and robust quantum networks that are essential for the future of quantum communication.
One of the primary hurdles in establishing quantum networks has been the preservation of entangled states over long distances in fiber environments. Previous attempts at transmitting entangled photons were hindered by excessive noise and polarization drift, making it impossible to maintain entanglement consistently. The team at Qunnect addressed this challenge by designing a network that operated with a high degree of stability under real-world conditions, as documented in their work published in PRX Quantum.
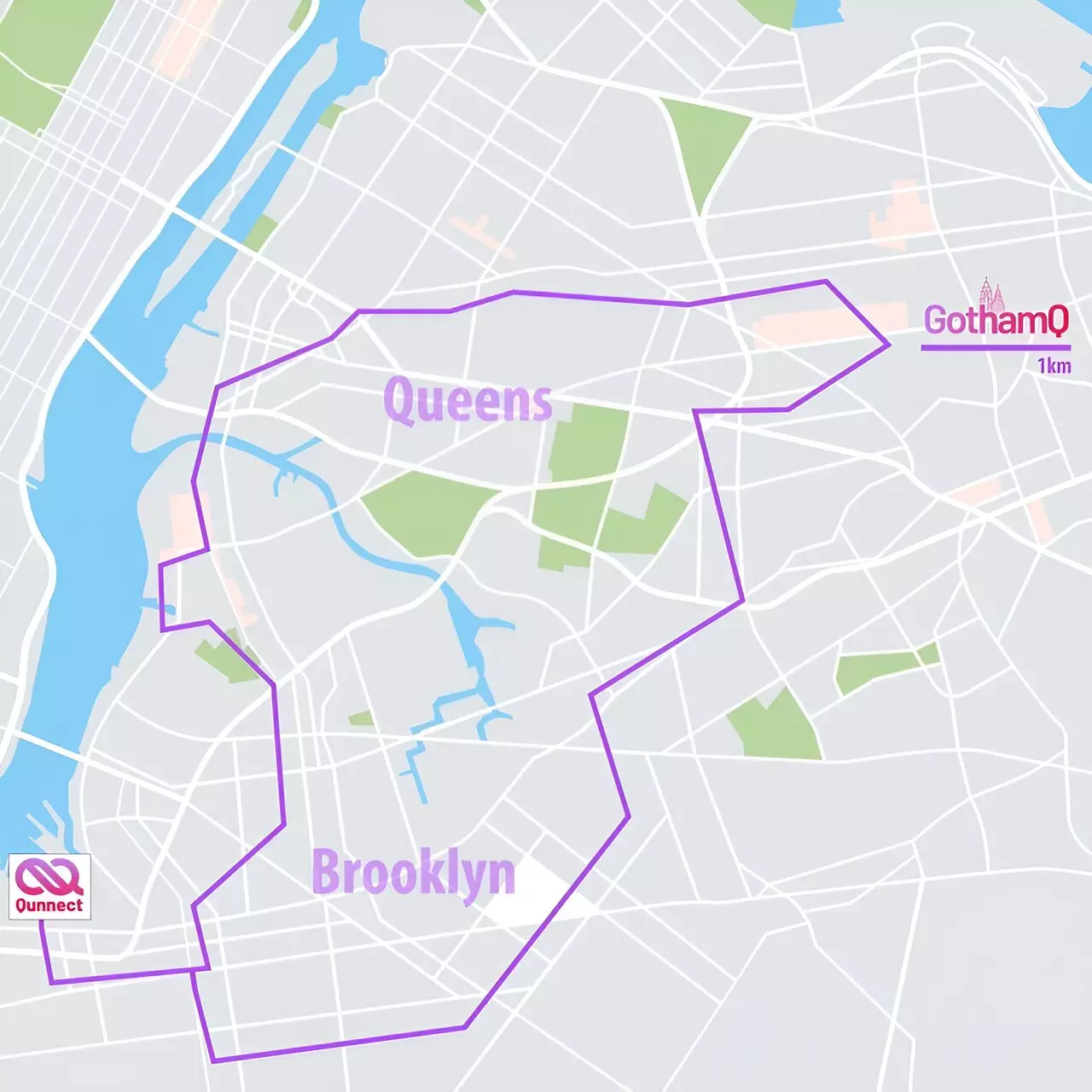
The researchers at Qunnect utilized a leased 34-kilometer-long fiber circuit, known as the GothamQ loop, to demonstrate the potential of their quantum network prototype. By using polarization-entangled photons, they were able to achieve an impressive uptime of 99.84% over a continuous operation period of 15 days. The network transmitted entangled photon pairs at a rate of approximately 20,000 per second, with a compensation fidelity of 99%. Remarkably, even at a higher transmission rate of half a million entangled photon pairs per second, the fidelity remained close to 90%.
Polarization-entangled photons play a critical role in quantum communication due to their ease of creation, manipulation, and measurement. These photons have been instrumental in developing large-scale quantum repeaters, distributed quantum computing, and quantum sensing networks. In the design by Qunnect, an infrared photon with a wavelength of 1,324 nanometers is entangled with a near-infrared photon of 795 nm, which is compatible with rubidium atomic systems used in quantum memories and processors.
A significant challenge faced by the team was the wavelength and time-dependent polarization drift in the system, requiring them to develop equipment for active compensation at specific wavelengths. To generate entangled dual-colored photon pairs, input beams of certain wavelengths were directed through a vapor cell enriched with rubidium-78. The resulting photons were then sent through the fiber in superpositions, representing a two-qubit configuration known as a Bell state.
To counteract disturbances in polarization caused by external factors such as vibrations, bending, and fluctuations, the researchers implemented automated polarization compensation (APC) devices. By sending classical photons down the fiber, they could measure and correct polarization drift at different transmission distances. This innovative approach not only improved the stability of the network but also reduced the need for manual recalibrations.
The success of Qunnect’s GothamQ loop demonstration represents a significant advancement towards establishing fully automated and practical entanglement networks essential for a quantum internet. By enhancing the stability and efficiency of quantum networks, researchers are paving the way for the widespread implementation of quantum communication technologies. The development of rack-mounted equipment by Qunnect signifies a crucial step towards making quantum networks accessible and applicable across various environments.
The recent achievements in quantum network stability and efficiency by the team at Qunnect showcase the immense potential of quantum communication technologies. As researchers continue to overcome challenges and innovate in this field, the realization of a robust and scalable quantum internet becomes increasingly feasible.