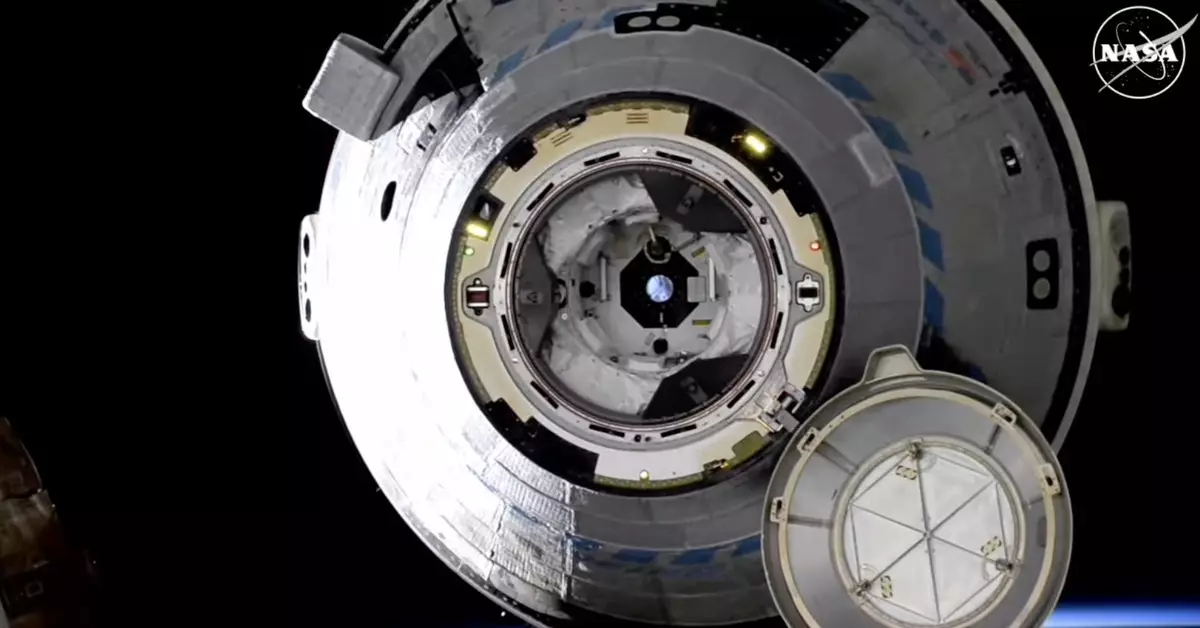
The Boeing Starliner spacecraft successfully completed its uncrewed flight back to Earth, as confirmed by NASA. However, it is important to note that this return occurred months later than originally intended. This delay raises questions about the efficiency and readiness of the spacecraft for future missions.
Impact on Original Crew
The delayed return of the Starliner also has implications for the original crew members, NASA astronauts Barry “Butch” Wilmore and Suni Williams. With the spacecraft’s return pushed back, Wilmore and Williams are now stranded aboard the International Space Station until the following year. This not only affects their personal schedules but also raises concerns about the sustainability of long-duration space missions.
While NASA officials have expressed pride in the successful descent of the Starliner, it is essential to critically analyze the reasons behind the delays and issues faced during the flight test. The learnings gained from this experience are valuable, but they also highlight the challenges and risks associated with space travel.
The original launch of the Starliner despite helium leaks already indicated potential technical challenges. Subsequent findings of additional leaks and issues with the spacecraft’s reaction control thrusters further underscore the importance of thorough testing and evaluation. As NASA prepares for future missions on the Starliner system, it is crucial to address these technical concerns to ensure the safety and success of astronauts.
Long-term Implications
Looking ahead, the delayed return of the Starliner and the extended stay of astronauts on the International Space Station have broader implications for NASA’s space exploration initiatives. The agency‘s collaboration with private companies like Boeing and SpaceX in the Commercial Crew Program has the potential to revolutionize space travel, but it also requires careful planning and risk management.
While the successful return of the Boeing Starliner spacecraft is a significant milestone, the delays and technical issues encountered during the flight test point to areas that need improvement. By critically analyzing these challenges and incorporating the learnings into future missions, NASA can enhance the safety and reliability of its space exploration endeavors.