As the influx of data continues to surge in today’s digital landscape, particularly within artificial intelligence (AI) systems, the demand for high-performance memory devices has become more critical than ever. These AI tools require not only substantial amounts of data to operate efficiently but also swift processing capabilities to facilitate real-time decision-making. Traditional memory systems, predominantly reliant on flash memory technology, often fall short of meeting these rigorous demands. Consequently, researchers are turning their attention to innovative memory solutions that can significantly enhance data transfer speeds while minimizing energy consumption.
High-bandwidth memory (HBM) technologies represent a promising avenue for elevating the performance of data storage in computing environments. By drastically improving the bandwidth between memory and processing units, these advanced systems hold the potential to streamline data transactions, allowing for quicker responses from AI applications. However, conventional flash memories, as they currently stand, struggle to keep pace with the high-speed requirements of emerging AI technologies. As a result, there is a pressing impetus for the development of ultrafast flash memory solutions that can redefine performance standards.
The transition from traditional flash memory to ultrafast alternatives is fraught with challenges. The industry is increasingly recognizing that while flash memory has been transformative in non-volatile data storage, its inherent limitations hinder its efficacy in supporting cutting-edge AI applications. Slow data transfer rates and restricted processing speeds prevent these devices from capitalizing on the full potential of AI-driven technologies. Therefore, researchers are actively exploring the application of two-dimensional (2D) materials as a means to fabricate faster and more efficient memory devices.
Recent investigative efforts have uncovered that certain 2D materials exhibit exceptional properties for constructing high-speed flash memory. These materials allow for the development of devices that can function at speeds previously unattainable with traditional silicon-based memories. Yet, while the potential benefits of 2D flash memory are promising, integrating these technologies into scalable systems has been challenging. The complexities associated with interface engineering between different materials have hindered the realization of ultrafast, non-volatile flash solutions.
Researchers at Fudan University have recently made significant strides in overcoming these obstacles. Their groundbreaking study, published in *Nature Electronics*, reveals a novel approach to integrating ultrafast 2D flash memory devices successfully. Utilizing advanced processing techniques—including lithography, e-beam evaporation, and a specialized annealing process—this team managed to fabricate an impressive array of 1,024 flash-memory devices, achieving a yield rate exceeding 98%. This achievement signals a notable advancement in the scalable production of high-performance memory technologies.
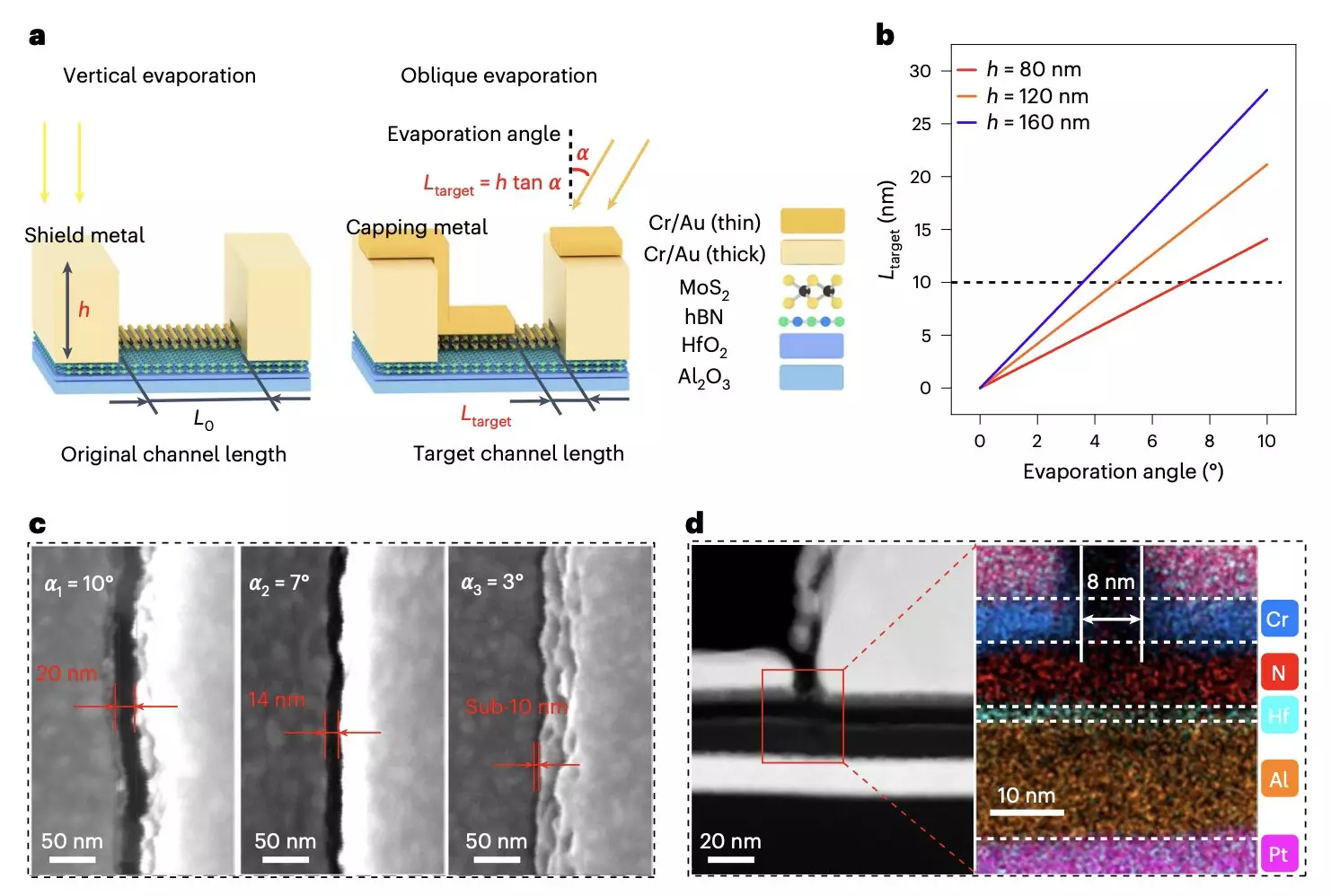
The researchers highlight their progress as they implemented two different tunneling barrier configurations utilizing monolayer molybdenum disulfide—a prominent 2D material. Not only did their devices maintain ultrafast operational speeds, but their innovative approach also allowed for channel lengths that could be scaled down to sub-10 nm, which is a significant improvement over current silicon flash memory limitations.
The implications of this research extend far beyond mere academic interest. As the technology matures, future studies could focus on utilizing various 2D materials to fabricate flash memory arrays, potentially revolutionizing the memory sector. With reliable, ultrafast flash memory solutions on the horizon, the ability to support AI-driven systems with the necessary speed and efficiency may soon become a reality.
Furthermore, the transition to these advanced memory devices could ameliorate some of the critical challenges currently faced within the AI domain, promoting faster data processing and resilience in non-volatile storage. This evolution in memory technology is likely to underpin a new era of AI innovations, with significant ramifications for numerous sectors reliant on high-performance computing and data analytics.
As researchers continue to unveil the potential of ultrafast 2D flash memory, the future of data storage looks promising. The scalable integration process adopted by Fudan University exemplifies how collaborative research and innovative technology hold the key to overcoming obstacles in memory performance, creating a foundation for more advanced applications in AI and beyond.