For individuals, the act of retrieving a book from a shelf appears trivial and instinctual. However, upon closer inspection, this seemingly simple action underscores a sophisticated cognitive process. It involves a considerable degree of planning, spatial awareness, and the ability to navigate around obstacles. In stark contrast, robotics has historically struggled with replicating this seamless fluidity of movement. Engineers and researchers have grappled with the concept of motion planning, which refers to the calculated effort involved in facilitating a robot’s ability to transport an object across a space populated with potential hindrances. The distinction lies in human adaptability; unlike robots, humans can dynamically adjust their actions according to the immediate environment, making the need for advanced motion planning all the more pressing in robotics.
Conventional motion planning algorithms pose numerous challenges due to their inherent limitations. Generally, these strategies require extensive computations, often involving thousands or millions of collision checks per task. This inefficiency is particularly pronounced in unpredictable environments where a robot must react on-the-fly. Not exclusively are these algorithms slow, but they also struggle to operate effectively in unpredictable settings – illustrating the stark contrast between human and robotic adaptability. For example, if a robot encounters a new obstacle—say a curious dog or a misplaced vase—it often finds itself unable to react swiftly or appropriately.
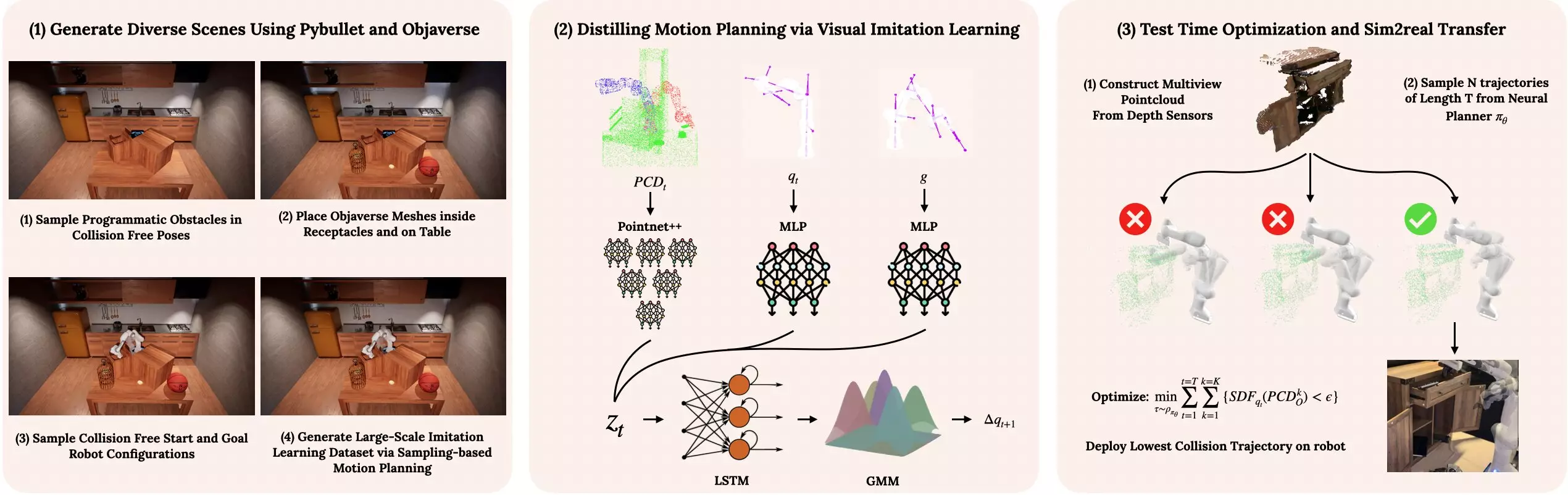
Responding to these challenges, researchers from Carnegie Mellon University’s Robotics Institute have introduced an innovative framework known as Neural Motion Planning. This approach drastically reconfigures how robots engage with new environments. By leveraging a single artificial intelligence (AI) network, this system not only facilitates motion planning but does so across various yet unfamiliar household settings. The ingenuity of this design lies in its data-driven nature, which mirrors the human learning process. Just as individuals hone a new skill through a combination of slow and deliberate practice followed by rapid execution, Neural Motion Planning allows robots to develop similar proficiencies.
To develop Neural Motion Planning, researchers undertook the monumental task of simulating millions of diverse household scenarios. The scenarios included navigating baker’s racks, avoiding kitchen appliances, and maneuvering through cluttered spaces. This rigorous training helped fine-tune the robots, allowing them to not only learn how to navigate environments like cabinets and dishwashers but also adapt to unforeseen obstacles. The models were further distilled into a generalist policy, empowering the robots to function in environments that they had not previously encountered.
This diverse training regimen provides the robot with a robust understanding of its surroundings. When deployed, it now possesses the ability to engage in reactive motion planning at high speeds, thus imitating the fluidity of human movement. Researchers like Jiahui Yang have lauded the success of this development, voicing excitement over the model’s capacity to deftly navigate any number of household obstacles to complete specific goals. Such achievements reflect a crucial advancement for robotics—one that aligns closer to human capabilities.
While progress in robotics has made substantial strides—particularly in areas such as vision and language with developments akin to ChatGPT—it is clear that similar advancements remain in earlier stages within the field of robotics. Neural Motion Planning represents a significant leap toward bridging the gap between human-like adaptability and robotic functionality. As Deepak Pathak, an influential figure within the Robotics Institute, noted, this work marks the beginning of a journey that could reshape how robots perceive and interact with the world around them.
The implications of successful motion planning could extend far beyond mere household applications. Whether in manufacturing, medical fields, or even autonomous vehicles, equipping robots with the capacity to adapt dynamically promises a variety of opportunities. In essence, the exploration of Neural Motion Planning not only serves to augment the capabilities of robotic systems but also paves the way for a future where robotics can integrate seamlessly into everyday life.