Quantum computing, although in its infancy, holds the potential to revolutionize numerous fields by leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics. Recent efforts by researchers from prominent institutions, including Freie Universität Berlin, NIST, and Google AI, highlight the significant strides made in estimating Hamiltonian parameters related to bosonic excitations within superconducting quantum systems. This article analyzes the methodologies employed in their groundbreaking research, shedding light on the implications for future quantum simulations and technologies.
Understanding Hamiltonians, which govern the dynamics of quantum systems, is pivotal for accurate quantum simulation. Historically, acquiring the Hamiltonian’s parameters has proven to be a complex endeavor, impacted by various factors such as measurement precision and computational limitations. Jens Eisert, the lead author of the study, initially underestimated the challenges posed by this task; however, as he delved deeper into the problem, it became evident that the intricacies involved would necessitate innovative solutions and collaborative expertise.
Eisert’s engagement began with a call from colleagues struggling with calibration issues on Google AI’s Sycamore quantum chip. These issues underscored the need for robust methods of Hamiltonian learning, prompting the researchers to devise actionable strategies to overcome the obstacles presented.
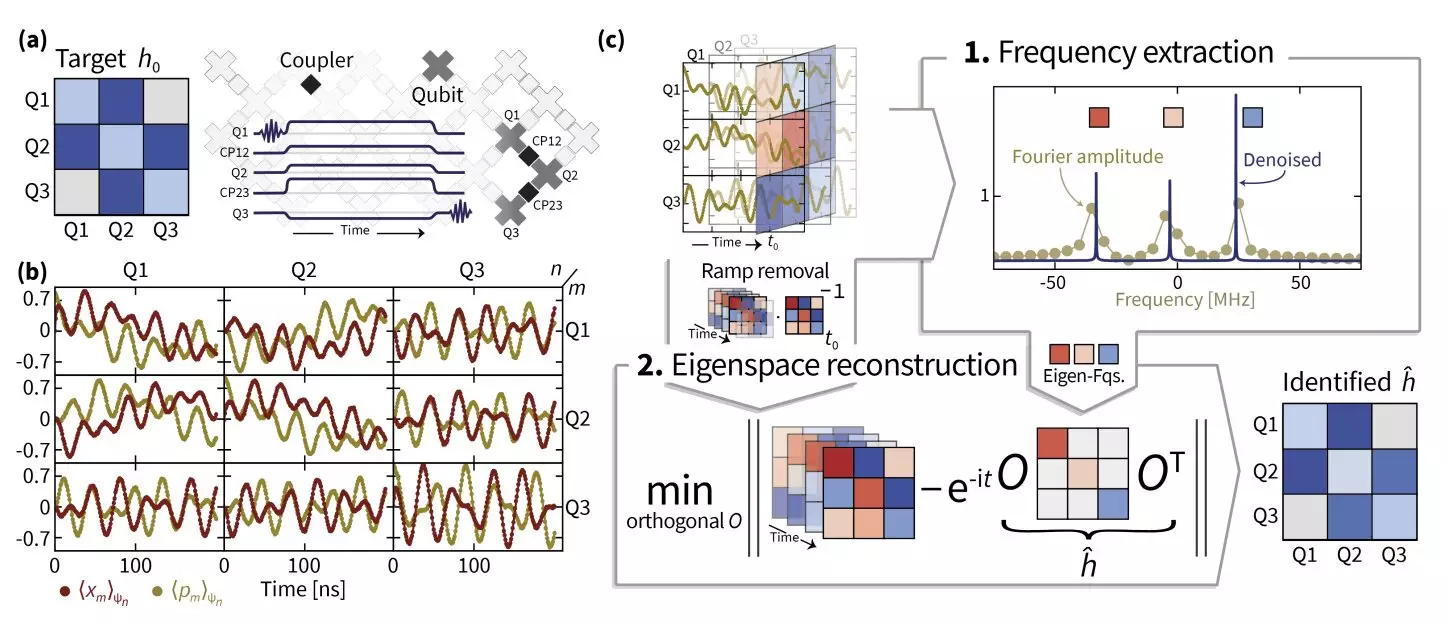
The research team systematically employed a series of advanced techniques to enhance their understanding of the Hamiltonian dynamics in their quantum simulator. Central to their approach was the concept of superresolution, a technique traditionally used in imaging that allows for enhanced resolution of eigenvalue estimations. This proved critical for accurately determining the frequencies necessary for Hamiltonian recovery.
Additionally, the team implemented manifold optimization, an advanced mathematical method suitable for solving complex problems where variables conform to a manifold rather than conventional Euclidean space. This approach facilitated the extraction of eigenspaces associated with the Hamiltonian operator, yielding more precise Hamiltonian information.
A significant breakthrough emerged with the development of TensorEsprit, a novel method that served as a synthesis of superresolution techniques and manifold optimization. This combination enabled the researchers to successfully recover Hamiltonian parameters for up to 14 coupled superconducting qubits, laying the groundwork for not only theoretical advancements but also practical applications in quantum computing.
Eisert and his team’s research underscores the paramount importance of ensuring the robustness and scalability of their Hamiltonian learning techniques. Early phases of their experimentation led to insights about the requisite accuracy of eigenvalue information for effective eigenspace recovery. Their journey unveiled a common theme in the field: the challenges of publishing findings associated with Hamiltonian learning stem from the inherent difficulties of applying these methods to practical datasets.
During this process, the researchers emphasized the necessity of improving signal processing techniques to allow for large system applications—this not only enhances the reliability of Hamiltonian parameter estimates but also facilitates the exploration of larger quantum processors. Their findings suggest that while challenges remain, the methodologies they established could pave the way for related advancements in characterizing quantum processors.
Looking forward, the research team aims to extend their methodologies to encompass interacting quantum systems and systems composed of cold atoms, a realm previously explored by physicist Immanuel Bloch. The potential for their techniques to contribute to broader questions regarding the nature of Hamiltonians may open new avenues for investigation and understanding in quantum mechanics.
This investigation into Hamiltonians is not merely academic; it has profound implications for quantum technologies. As quantum simulations become increasingly sophisticated, the insights derived from enhanced Hamiltonian learning techniques can inform the development of applications that rely on accurate modeling of complex quantum systems. The researchers envision these advancements facilitating analog quantum simulations that would allow scientists to probe quantum materials and phenomena under meticulously controlled laboratory conditions.
The pioneering work conducted by Eisert and his collaborators not only illuminates the intricacies of Hamiltonian learning but also sets a precedent for future research in the quantum domain. By overcoming significant obstacles in Hamiltonian recovery, they have created a foundation that promises to enhance both theoretical understanding and practical applications in quantum computing.
As the field progresses, the ability to accurately characterize Hamiltonians could yield transformative insights, ushering in a new era of exploratory research into quantum phenomena that were once thought to be beyond reach. In essence, this work does not merely represent a technical achievement but rather a visionary leap towards harnessing the full potential of quantum technology, with implications that may extend far beyond the realm of physics.