In the intricate realm of quantum computing, the information processed by qubits is notoriously delicate. This fragility poses significant challenges during experimental procedures, particularly when accidental measurements can cumbersome destroy the quantum state. Among the various strategies employed to mitigate these risks, protecting qubits from unintentional interference is an essential aspect of maintaining the integrity of quantum operations. As researchers make strides in quantum error correction protocols, the need for effective measurement techniques without disturbing neighboring qubits has become paramount.
Current methods often involve trade-offs that can compromise the coherence time of qubits, lead to wastage of resources, or inadvertently introduce errors. Each of these factors hinders the ambitious target of developing robust quantum systems capable of reliably processing information. Thus, progress in this arena is vital for overcoming the inherent challenges of quantum technologies and propelling the field forward.
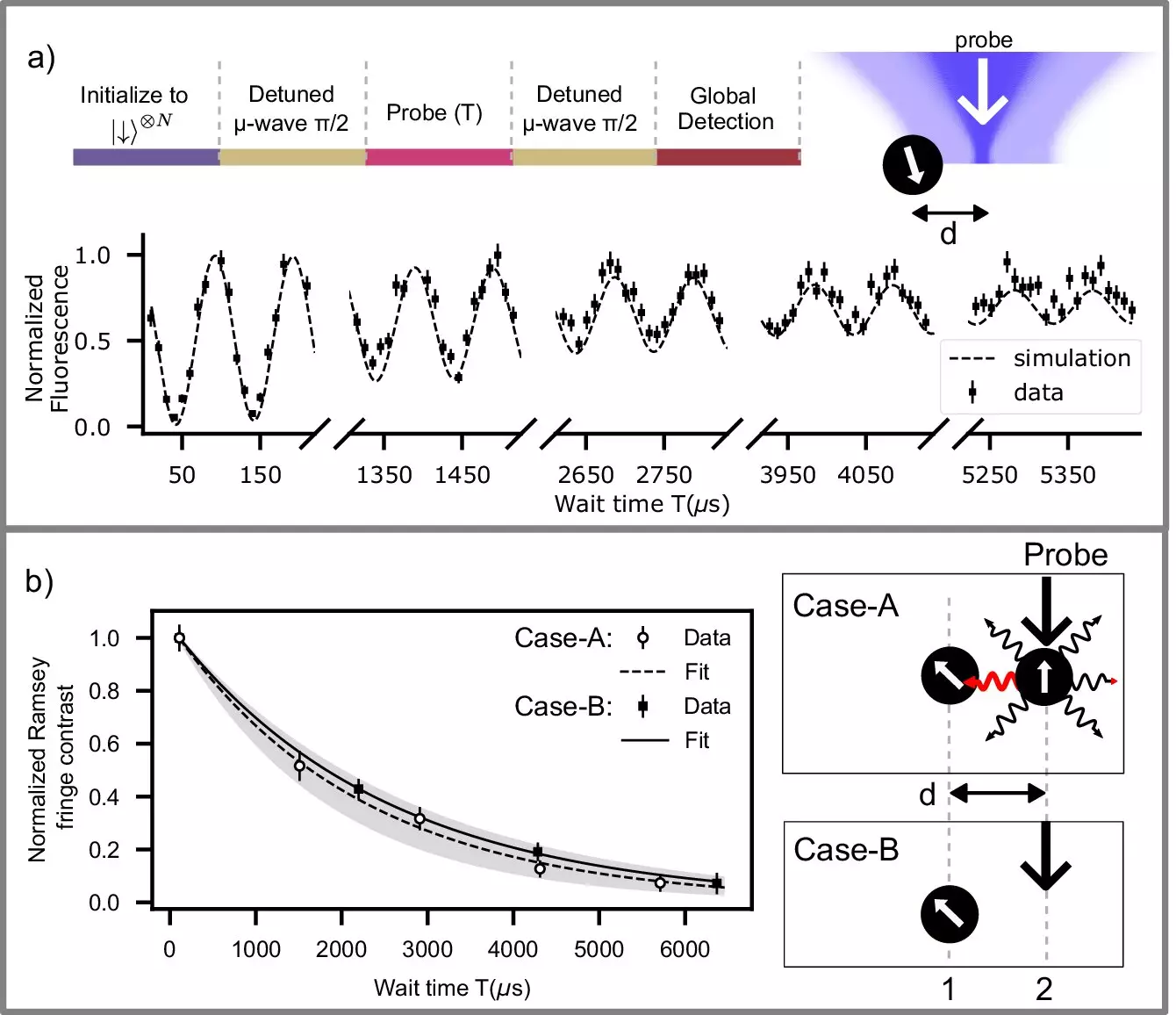
Amid these challenges, a team of researchers from the University of Waterloo has made a compelling advancement that could transform the field of quantum information science. Led by Rajibul Islam at the Institute for Quantum Computing, the team’s recent findings, published in *Nature Communications*, reveal a method for measuring and resetting a trapped ion qubit with unprecedented precision. This technique allows them to operate without degrading the states of neighboring qubits that are mere micrometers away—distances smaller than the width of a human hair.
This remarkable achievement represents a quantum leap in experimental physics, suggesting that qubit manipulation can be achieved with minimal risk of interference. The implications of such advancements extend well beyond immediate results; they may pave the way for enhanced quantum simulations, refined quantum processors, and improved error correction strategies in existing quantum computing architectures.
At the core of this innovative breakthrough lies the sophisticated application of laser technology. By honing their ability to control laser light with precision, the research team effectively navigated a challenge previously deemed insurmountable: the protection of vital qubits while measuring others in close proximity. The method leverages holographic beam shaping technology, developed in previous research endeavors, which enhances the control over light interactions with ions in an ion trap setup.
The success of the experiment hinged not only on technological sophistication but also on a reconstructive shift in the researchers’ mindset. Traditionally, the consensus in the quantum computing field was that minimizing disturbance was practically impossible when measuring qubits closely positioned together. However, the team’s rigorous exploration and innovative thinking have underscored the reality that such precision is attainable. Through advanced calculations and methodologies, they have identified a way to maintain coherence in qubits while ensuring reliable measurement outcomes.
The empirical results from this experimentation demonstrate the high fidelity of qubit preservation while executing measurements. The researchers achieved an astounding accuracy of over 99.9% in safeguarding an “asset” ion qubit while resetting a neighboring “process” qubit, as well as over 99.6% fidelity during a photon detection beam applied to the adjacent qubit. These figures highlight the potential for unimaginably accurate quantum operations and suggest significant improvements over earlier methods, which often required physically distancing qubits to mitigate interference.
This precision is especially noteworthy when considering that many previous attempts to perform measurements while maintaining qubit integrity necessitated physically moving qubits hundreds of microns away. This approach not only introduces delays into experimental setups but can also add noise, diminishing overall system performance. The Waterloo researchers’ revelation that close-proximity measurement is feasible invites a reevaluation of established paradigms in the quantum computing landscape.
As the impact of this breakthrough resonates through the quantum computing community, its potential applications are vast. By mitigating the risks associated with qubit measurements, this research lays the groundwork for robust implementations of quantum error correction, enhancing the viability of larger quantum systems and facilitating more advanced quantum simulations. The ability to conduct controlled, high-fidelity measurements could lead to more reliable quantum processors and breakthrough advancements in quantum information theory.
Moreover, the incorporation of middle-circuit measurements with controlled light can harmoniously integrate with existing quantum technologies. Approaches that involve relocating essential qubits or leveraging quantum states that remain untargeted by measurement beams can further amplify the effectiveness of this technique, ensuring that research continues to propel the quantum computing field toward unprecedented heights.
These pioneering efforts by the University of Waterloo research team not only address the challenges of qubit protection but also signal a transformative moment in the evolution of quantum computing. With continued innovation, the future of quantum technology holds the promise of unlocking the vast potential of quantum systems to reshape the landscape of computational science.