In recent years, the prevalence of solar panels adorning rooftops and sun-soaked energy farms has surged, signaling a pivotal shift in how we harness renewable energy. Even in countries like the UK, notorious for its gray skies and drizzly weather, solar energy is emerging as an influential force in electricity generation. Fueled by rapid advancements in technology and unprecedented improvements in power conversion efficiency, solar energy is not just a fleeting trend but a fundamental player in our energy landscape.
What propels this growth? Two primary factors stand out: first, the evolution of manufacturing processes that allow for the mass production of solar panels at remarkably low costs, and second, ongoing breakthroughs in efficiency that maximize the amount of sunlight converted into usable electricity. The questions linger: how efficient can solar panels realistically become, and will these advancements yield noticeable financial benefits for consumers?
The Current Landscape of Solar Panel Efficiency
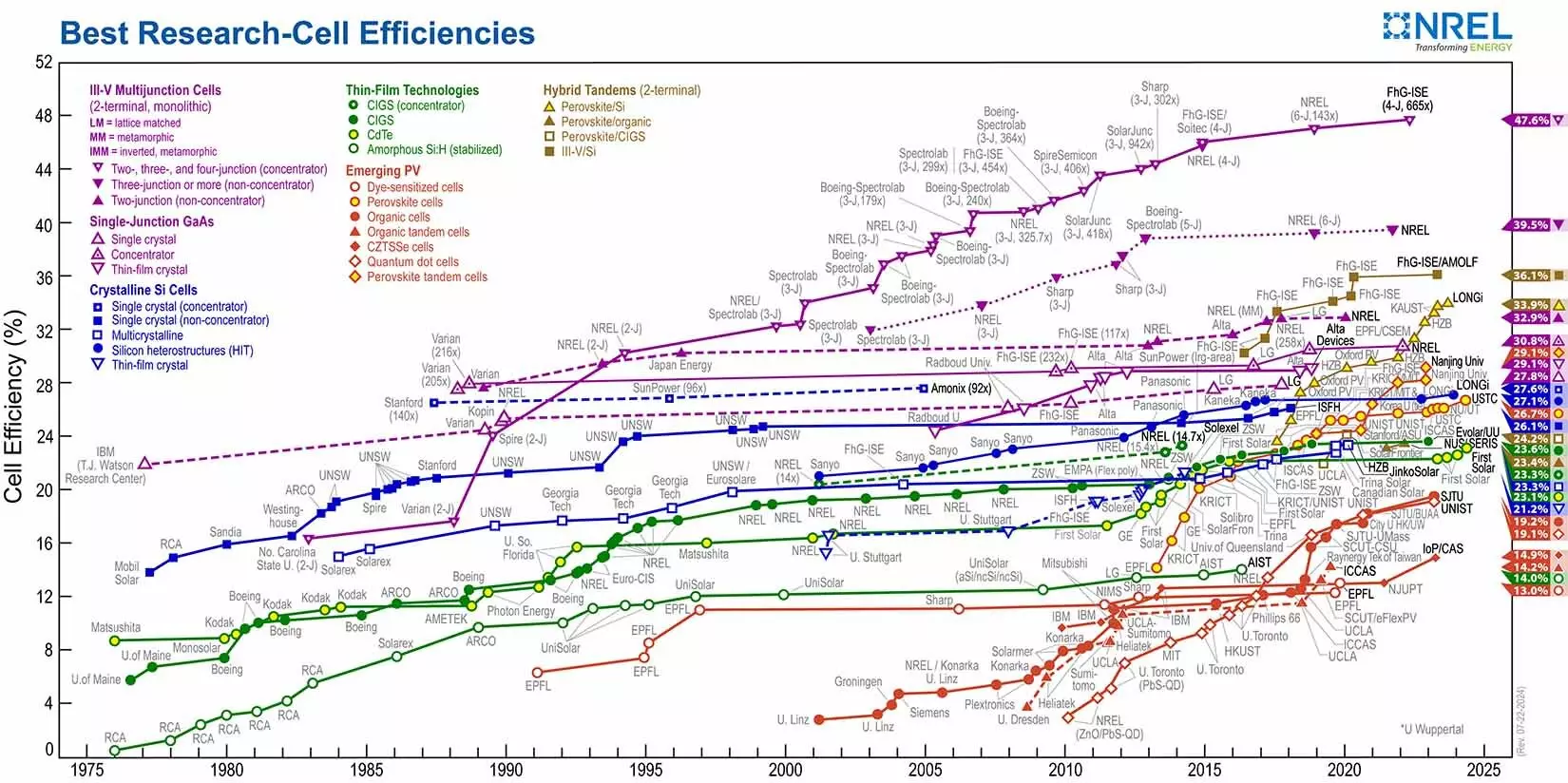
As it stands, conventional solar panels boast an efficiency rating between 20% and 22%, meaning that only a fraction of available sunlight is transformed into electrical power. However, pioneering research published in the journal *Nature* hints at a bright future where solar panels could reach astonishing efficiencies of up to 34%. This breakthrough hinges on the innovative application of tandem solar cells—an advancement that could redefine the renewable energy sector.
Traditional solar cells are crafted using a singular material, typically silicon, which is the same substance that powers our electronic devices. While silicon remains a reliable and widely used resource, its efficiency has a ceiling of about 29%. To surpass this limit, scientists have developed tandem solar cells that stack multiple layers of solar materials, allowing them to capture a broader spectrum of sunlight.
Recent discoveries by researchers at the energy powerhouse LONGi have unveiled a tandem cell that synergistically combines silicon with perovskite materials, achieving a groundbreaking efficiency of 33.89%. Perovskite materials, characterized by their versatile light absorption properties, efficiently capture high-energy blue light—an aspect that enhances the overall tandem efficiency and minimizes energy losses.
Despite the impressive strides made with perovskite-silicon tandem cells, remarkable efficiencies alone are not enough to ensure widespread adoption. The production of these advanced cells poses significant challenges; while they can achieve superior performance, the manufacturing process must be both scalable and cost-effective. Current perovskite solar cell prototypes are small and constructed in controlled lab environments, far from the scalability required to power households and industries.
The transition from laboratory successes to commercial viability necessitates critical innovations that can deliver large-scale, durable panels ready for real-world conditions. Leading the charge, Oxford PV—a pioneer in perovskite solar technology—has recently made strides in addressing integration issues and enhancing panel longevity. Yet, the goal of achieving 34% efficiency in commercially available designs remains an ambitious goal.
Furthermore, while the advancements in solar technology herald a greener future, the sustainability of the materials used in tandem solar panels raises important concerns. The extraction and processing of essential components such as lead, carbon, iodine, and indium can be energy-intensive and environmentally detrimental. As the industry evolves, balancing efficiency advancements with responsible sourcing of materials will be pivotal in ensuring that solar energy remains a truly sustainable solution.
One of the most compelling aspects of higher efficiency solar panels lies in their potential impact on consumer energy costs. With increased efficiencies, the financial incentive for homeowners to adopt rooftop solar becomes increasingly attractive. An analysis suggests that if solar panel efficiency rises from an average of 22% to 34%, annual electricity bill savings for a typical British household could soar from £558 to £709—a substantial increase that could trigger a surge in solar installations.
However, the reality of consumer electricity pricing complicates the situation. In the UK, electricity prices are determined by a complex matrix that may not fully reflect the savings accruing from enhanced generation capabilities. For homeowners investing in rooftop solar, navigating these economic intricacies while maximizing energy independence through battery storage or net metering will be critical.
Despite the challenges inherent in scaling up tandem solar technology, the trajectory is clear: solar energy is set to play a pivotal role in our global transition to renewable systems. With efforts in research and development continuously pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, the integration of solar technology into various applications—from residential homes to electric vehicles—opens new avenues for sustainable energy.
As scientists and engineers work collaboratively to surmount remaining hurdles, a future powered by efficient solar energy moves closer to reality. The journey to enhanced efficiency, sustainable material sourcing, and economic feasibility is essential for making solar technology a central pillar of our clean energy infrastructure. The progress made thus far is promising, but the road ahead will require innovation, commitment, and an unwavering focus on sustainability. Ultimately, it’s not just about reaching new efficiencies; it’s about paving the way for a greener planet.