Spintronics, or spin transport electronics, represent a transformative shift in how we approach technology, particularly in terms of computing. Unlike traditional electronics that rely on the movement of electric charge to transmit information, spintronics harnesses the intrinsic spin of electrons alongside their charge. This dual approach potentially yields a new class of devices that not only mimic the speed of conventional electronics but also offer superior energy efficiency. Emerging from ongoing research, this field is poised to revolutionize how we think about information processing, memory storage, and energy consumption across various technologies.
Despite its promising future, the deployment of spintronic devices faces hurdles, particularly concerning the effects of temperature on their operation. The core inquiry centers around an essential question: How does heating influence the behavior of these devices? The ability of a spintronic device to alter its magnetization using electric currents is influenced not only by electromagnetic interactions but also by the heat generated through these currents. Understanding this relationship is critical, as it informs material selection and device engineering.
Axel Hoffmann, a notable figure in this research area, posits that distinguishing between these two mechanisms—current-driven versus thermally driven changes—can significantly impact device performance. If spin changes are primarily influenced by current, engineers can focus on improving the speed across devices. Conversely, if thermal effects dominate, challenges related to heat management could impose limitations on the speed of operation, necessitating a reevaluation of design strategies.
Until recently, progress in addressing these challenges has been hampered by the lack of effective techniques to measure heating in small-scale spintronic devices directly. Traditional methods often fall short when it comes to discerning how temperature influences electrical and magnetic operations at the micro-level. In an exciting development, researchers from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have introduced a novel experimental approach that quantifies the heating effects in antiferromagnetic materials.
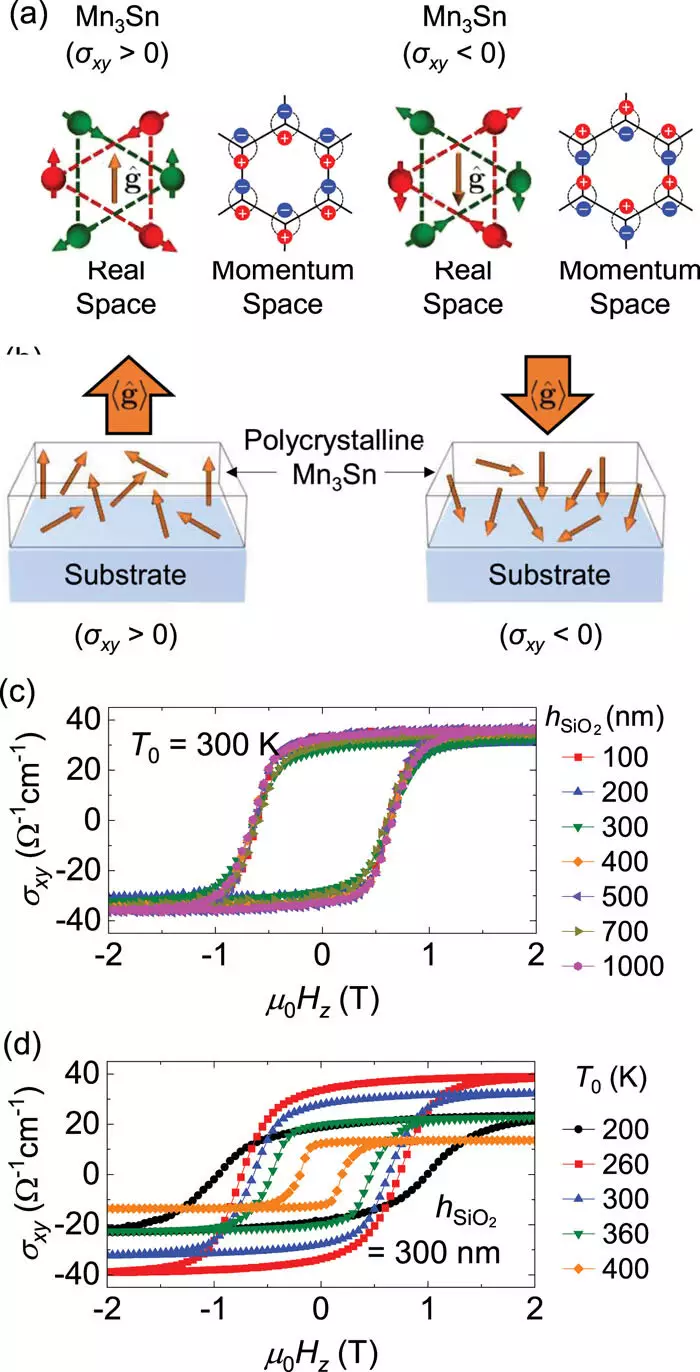
Postdoctoral researcher Myoung-Woo Yoo led the initiative to analyze how thermal dynamics play a role in spintronic devices. By manipulating the thermal conductivity of substrates on which antiferromagnetic materials are placed, the researchers could delineate the heating effects more clearly. They used silicon dioxide substrates of varying thicknesses, noting that the thicker a substrate, the more pronounced the heating effect when subjected to the same electric current. This method allows for a systematic assessment of different spintronic materials, paving the way for deliberate selection based on how minimally their magnetic properties are affected by heat.
The implications of this research extend far beyond theoretical discussions. The findings indicate that heat significantly influences the behavior of certain antiferromagnetic materials, which raises important considerations for device design. Researchers observed notable interaction effects in Mn3Sn, one of the antiferromagnetic materials studied. Understanding how this and other substances respond to heat can help in selecting materials that retain their functional integrity under operational stresses.
Moreover, as the understanding of thermal dynamics in these systems grows, it offers a roadmap for creating more robust and efficient spintronic devices. The methodology developed by Hoffmann’s team not only aids in evaluating existing materials but also prompts exploration into other promising candidates for future applications. As spintronics merges more closely with traditional electronics, the potential for hybrid systems that combine the best aspects of both fields becomes increasingly feasible.
The ongoing research into spintronics underscores a pivotal moment in the development of future computing technologies. With advancements in measuring and understanding heating effects, researchers are equipped to optimize these devices for better speed and energy efficiency. As the boundary between conventional electronics and spintronics blurs, we inch closer to realizing a technology that leverages the strengths of both realms. The collaboration among physicists, engineers, and material scientists will be key to unlocking the full potential of spintronics, leading to groundbreaking applications that range from faster computers to energy-efficient memory systems. Thus, the journey into spintronics not only reshapes our current technological landscape but also opens up possibilities for innovations that could define the future of electronic devices.