Deep learning has emerged as a game-changing technology across various industries, including healthcare, finance, and beyond. These models, powered by neural networks, exhibit unprecedented capabilities in tasks ranging from diagnosing diseases to predicting market trends. However, as the reliance on deep learning grows, so does the necessity for substantial computational resources. Most organizations turn to cloud-based solutions to meet these demands. While this enables access to powerful computing, it also introduces serious security vulnerabilities, particularly in sensitive domains like healthcare, where patient privacy is of utmost concern.
The reliance on centralized cloud servers for deep learning exposes confidential data to potential breaches. In healthcare, for instance, hospitals may struggle to justify the use of AI tools that analyze private patient information. Concerns arise regarding whether cloud providers can ensure the security of this data, especially given the increasing prevalence of cyberattacks. Thus, the need for innovative solutions that ensure the integrity of sensitive information during deep-learning practices has never been more critical.
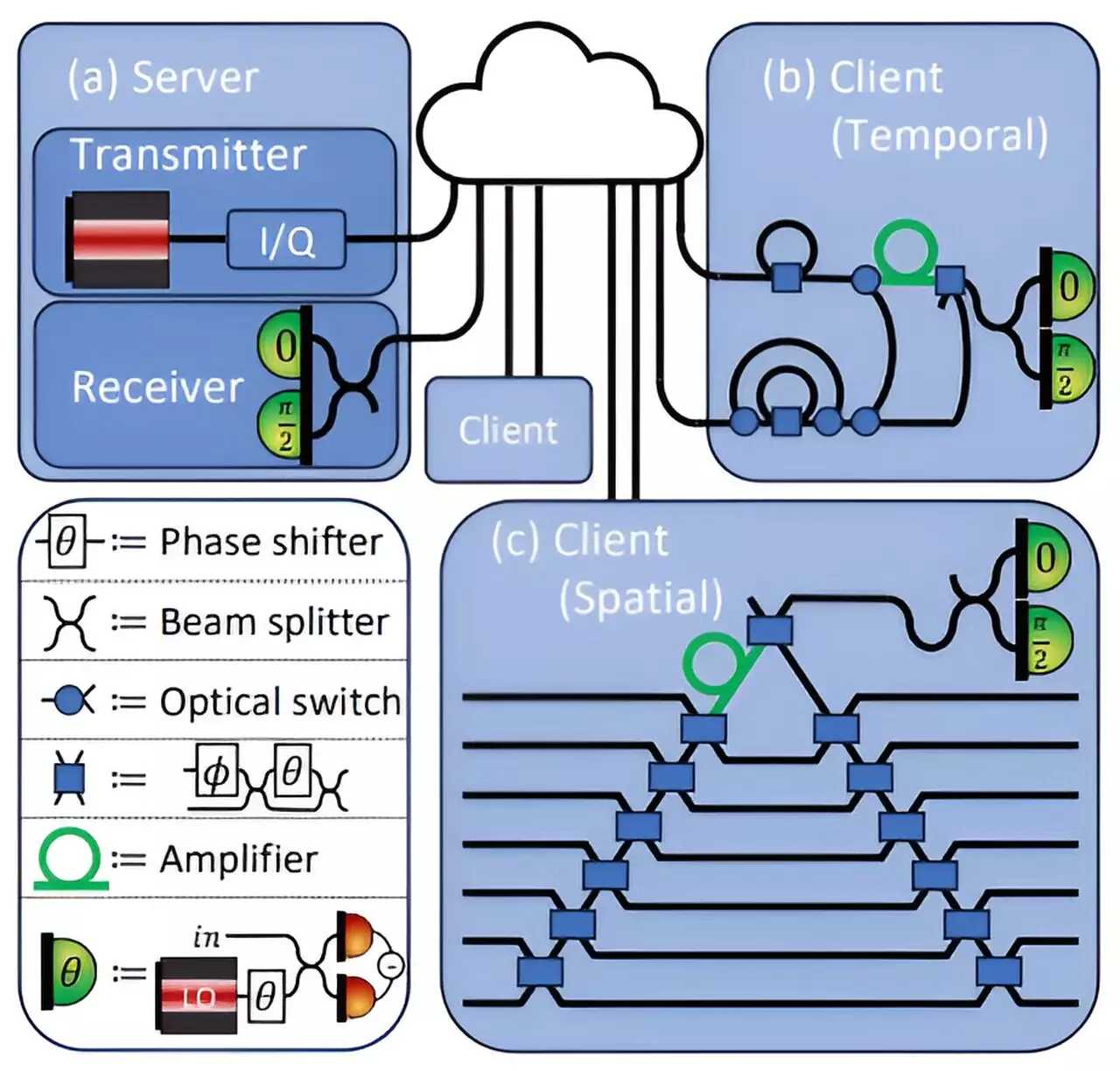
Researchers at MIT have taken a significant stride toward addressing these challenges through the development of a pioneering security protocol grounded in quantum mechanics. This protocol employs the unique properties of quantum light to safeguard data during transmission between clients and cloud servers. By encoding essential information into the laser light utilized in fiber optic communication, the protocol ensures that any attempt to intercept or clone this data is impossible without detection, thanks to the no-cloning theorem inherent to quantum mechanics.
At the heart of this groundbreaking security approach is the way deep neural networks operate. A neural network consists of multiple interconnected layers, where each node conducts computations on incoming data. The MIT researchers devised a method to encode these ‘weights’—the variables determining how a neural network processes data—into photon states. When a client seeks to perform an analysis using sensitive data, such as medical images, this encoded information is transmitted securely.
Importantly, the client interacts with the network outputs while ensuring that neither the client’s data nor the proprietary model remains exposed. This is achieved by allowing the client to measure only the minimum necessary output while actively preventing them from duplicating the transmitted weights. Furthermore, any minor errors introduced during this process are monitored by the server, providing an added layer of security. This innovative mechanism guarantees that confidential patient information is kept private while still allowing for high accuracy in predictions.
One of the most compelling aspects of this protocol is its ability to maintain a high level of accuracy in deep learning tasks. During testing, the researchers found that the system could uphold an impressive accuracy rate of 96% while ensuring that both client and server data remained secure. This accomplishment is significant because it removes the common apprehension associated with integrating advanced computational techniques into sensitive applications.
Moreover, the results showed that the protocol limits the potential information leaks to less than 10% of what an adversary would need to reconstruct any encrypted data from the client, providing robust safeguards against potential breaches. In a scenario where the server is compromised, it would only obtain about 1% of the necessary information to decipher client data.
Looking forward, the MIT team envisions applying their security protocol to broader contexts, such as federated learning. This technique enables multiple entities to collaborate on training a centralized deep-learning model while maintaining individual data privacy. The implications of this advancement are profound, as they could facilitate decentralized machine learning processes in domains like personalized medicine and collaborative financial models, where protecting participant data is paramount.
The pioneering work at MIT not only bridges the gap between deep learning and quantum cryptography but also promises to redefine how industries approach data security. As reliance on cloud computing and AI continues to expand, innovations like this are essential in paving the way toward ethical and secure digital environments. The collaboration between quantum mechanics and artificial intelligence may very well set a new standard for the maintenance of privacy in the digital age.