Solar energy has long been viewed as a promising renewable energy source, and advancements in technology have led to the development of various solar concentrator systems. One such innovation is the luminescent solar concentrator (LSC), which utilizes luminescent materials to convert and concentrate sunlight onto photovoltaic (PV) cells. While traditional concentrators rely on mirrors and lenses, LSCs have the unique advantage of being able to harvest diffuse light, making them ideal for applications such as building-integrated photovoltaics.
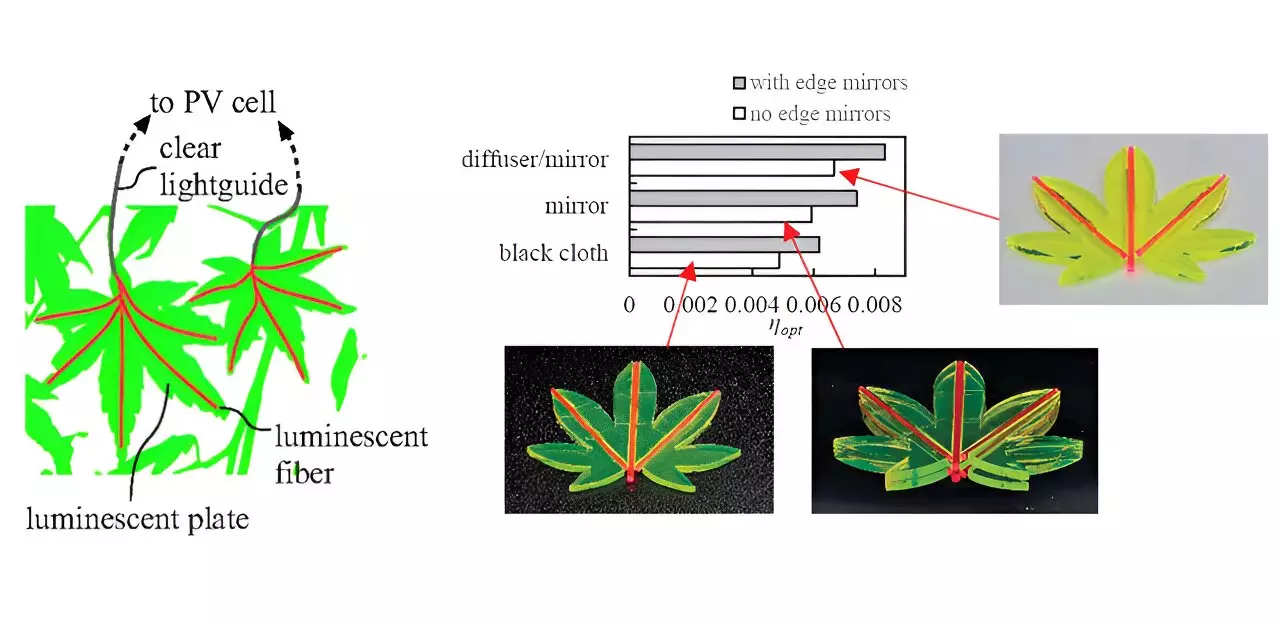
Recently, researchers at Ritsumeikan University in Japan have introduced a groundbreaking “leaf LSC” model that addresses the scalability challenges faced by traditional LSC designs. This innovative approach involves using smaller luminescent components that mimic the structure of leaves on a tree. By placing luminescent plates around a central luminescent fiber, with the plates’ sides facing the fiber, incident photons are converted into photoluminescent (PL) photons, which are then directed towards a PV cell at the tip of the fiber.
The leaf LSC design offers several advantages over traditional LSC systems. By reducing the lateral size of individual modules, researchers have found that the efficiency of photon collection can be significantly improved. For example, decreasing the side length of a square leaf LSC from 50 mm to 10 mm resulted in a marked increase in photon collection efficiency. Additionally, the modular design of the leaf LSC enables easy replacement of damaged units and integration of advanced luminescent materials as they become available.
To further enhance the efficiency of the leaf LSC, techniques from traditional planar LSCs, such as edge mirrors and tandem structures, have been incorporated into the design. Through experiments, researchers have demonstrated that the optical efficiency of these leaf-like structures can be calculated analytically based on the spectrum and intensity of incident light, using a single-spot excitation technique. This integration of traditional LSC techniques with the innovative leaf LSC model showcases a creative approach to driving sunlight towards adjacent photovoltaic devices.
Optimizing photon collection in LSCs through the leaf LSC approach holds promise for more flexible and scalable solar energy solutions. This innovative design has the potential to revolutionize the application of solar concentrators, making them more efficient and adaptable for various uses, from large-scale installations to building-integrated systems. As technology continues to advance, the leaf LSC model could significantly enhance the performance of solar energy systems, ultimately contributing to more sustainable energy solutions.
The development of the leaf LSC model highlights a creative and effective approach to enhancing solar energy capture. By combining scalable, bio-inspired designs with advancements in optical engineering, researchers are paving the way for more efficient and practical solar concentrator systems. As the technology evolves, the leaf LSC approach may play a critical role in shaping the future of solar energy solutions.