The combination of quantum entangled light sources and ultrafast stimulated Raman spectroscopy represents a cutting-edge advancement in the field of molecular analysis. These two technologies have gained significant momentum in recent years, each offering unique capabilities and applications in various domains. The fusion of these techniques provides a powerful analytical tool for studying complex molecular materials, enabling high-speed imaging of ultrafast processes within molecular systems.
Stimulated Raman spectroscopy is a modern analytical method used to study molecular vibrational properties and interactions. It is a member of the Raman process family and is based on the interaction between incident light and sample molecules, resulting in a frequency shift of the scattered light. The key breakthrough of stimulated Raman spectroscopy lies in its ultrafast processing capabilities, providing rapid acquisition of crucial molecular information.
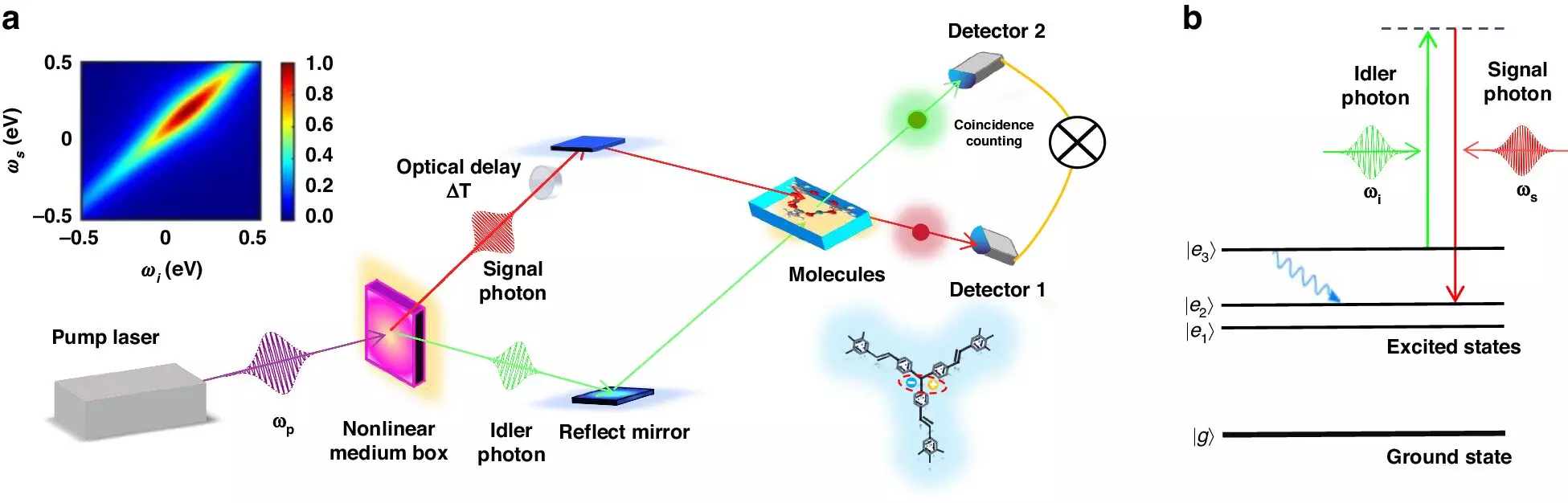
Quantum entangled photon sources play a vital role in stimulated Raman scattering, providing pairs of entangled photons that induce stimulated Raman scattering when interacting with matter. These sources offer non-classical properties, such as correlations between photon pairs in terms of time, frequency, or polarization. Leveraging entanglement enhances the frequency and temporal resolution of spectroscopic signals and enables super-resolved spectra with time-frequency scales beyond classical bounds.
The fusion of quantum entangled light sources and ultrafast stimulated Raman spectroscopy offers several advantages. By utilizing entangled photon sources, molecules actively serve as beam mixers for Raman pump and probe fields, resulting in a super-resolved spectrum with unprecedented selectivity in spectroscopic signals. This technique enables high-speed imaging of molecules, particularly those exhibiting ultrafast processes on the femtosecond timescale.
Future advancements in quantum spectroscopy are expected to yield profound breakthroughs in the field of quantum physics and quantum control at room temperature. These advancements will drive the development of more efficient and stable quantum light source generation technologies, impacting areas such as optical communication, quantum computing, and quantum sensing. The highly efficient and accurate spectral measurement methods derived from quantum spectroscopy are anticipated to play pivotal roles in diverse fields, including materials science, chemical reactions, and biomedical research.
The fusion of quantum entangled light sources and ultrafast stimulated Raman spectroscopy represents a groundbreaking concept in the field of molecular analysis. This innovative technique leverages the quantum advantages of entangled photon sources to enhance both the temporal and spectral resolution of spectroscopic signals, enabling high-speed imaging of ultrafast processes within molecular systems. By harnessing this fusion, deeper insights into molecular structural analysis and dynamic observation can be obtained, propelling significant progress in related domains.