Ethylene (C2H4) is a valuable compound used in various industries such as manufacturing, agriculture, and healthcare. The traditional methods of producing ethylene involve high-energy processes that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. However, researchers have recently introduced a new approach to ethylene production using solar-powered photocatalytic dehydrogenation of ethane.
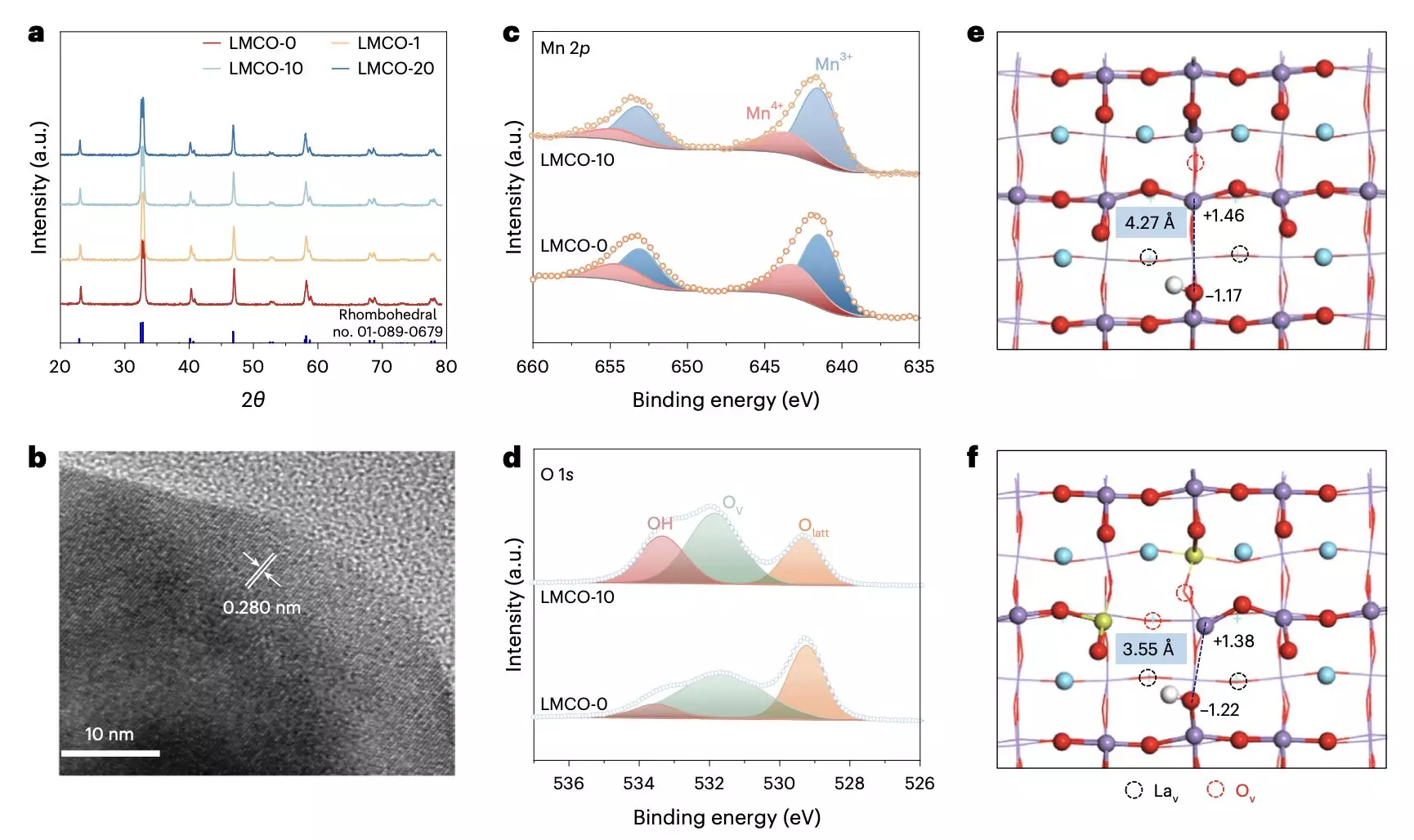
The study conducted by researchers at Soochow University, University of Toronto, and other institutes focused on utilizing the perovskite oxide LaMn1−xCuxO3 as a photocatalyst for converting ethane into ethylene and hydrogen under ambient conditions. This innovative method aims to reduce carbon emissions associated with traditional ethylene production processes.
The researchers demonstrated that the perovskite oxide exhibited redox-active Lewis acid sites and base sites, optimizing the activity, selectivity, and yield for ethane dehydrogenation. By using solar or LED lights for the conversion process, they achieved efficient ethylene production rates with lower carbon emissions compared to traditional methods.
The team tested their solar-powered ethylene production approach using a rooftop prototype device and conducted comprehensive technical and economic analyses. The results showed promising ethylene production rates and ethane conversion percentages, highlighting the economic potential of this innovative solution for large-scale ethylene production.
Moving forward, the researchers plan to further investigate the performance of the photocatalyst and photoreactor in catalytic reactions. They aim to improve photochemical activation, light capture, and light transport rates to enhance the photocatalytic efficiency of the LaMn1−xCuxO3 perovskite for future ethylene production processes.
The development of a solar-powered photocatalytic dehydrogenation method for ethylene production represents a significant step towards sustainable and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes. The use of innovative materials and renewable energy sources in chemical production is essential for reducing carbon footprints and addressing the increasing demand for versatile hydrocarbons like ethylene. As researchers continue to explore and optimize this technology, the future of ethylene production looks promising.