As society advances into an era marked by an insatiable appetite for data, conventional wireless communication methods are reaching their limits. Traditional radio frequency (RF) technologies, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, are increasingly burdened by bandwidth limitations and growing wireless congestion. Users frequently encounter dropped connections, latency, and inconsistent performance, particularly in densely populated areas or environments with multiple competing signals. The need for a scalable, reliable, and efficient solution is more pressing than ever.
The demand for faster and more dependable wireless communication is driving innovation in alternative technologies. One promising paradigm emerging from this search is Optical Wireless Communication (OWC), a transformative approach that leverages light instead of radio waves for data transmission. This emerging technology aims to address the deficiencies of RF systems and is poised to redefine the ways we interact with our digital environments.
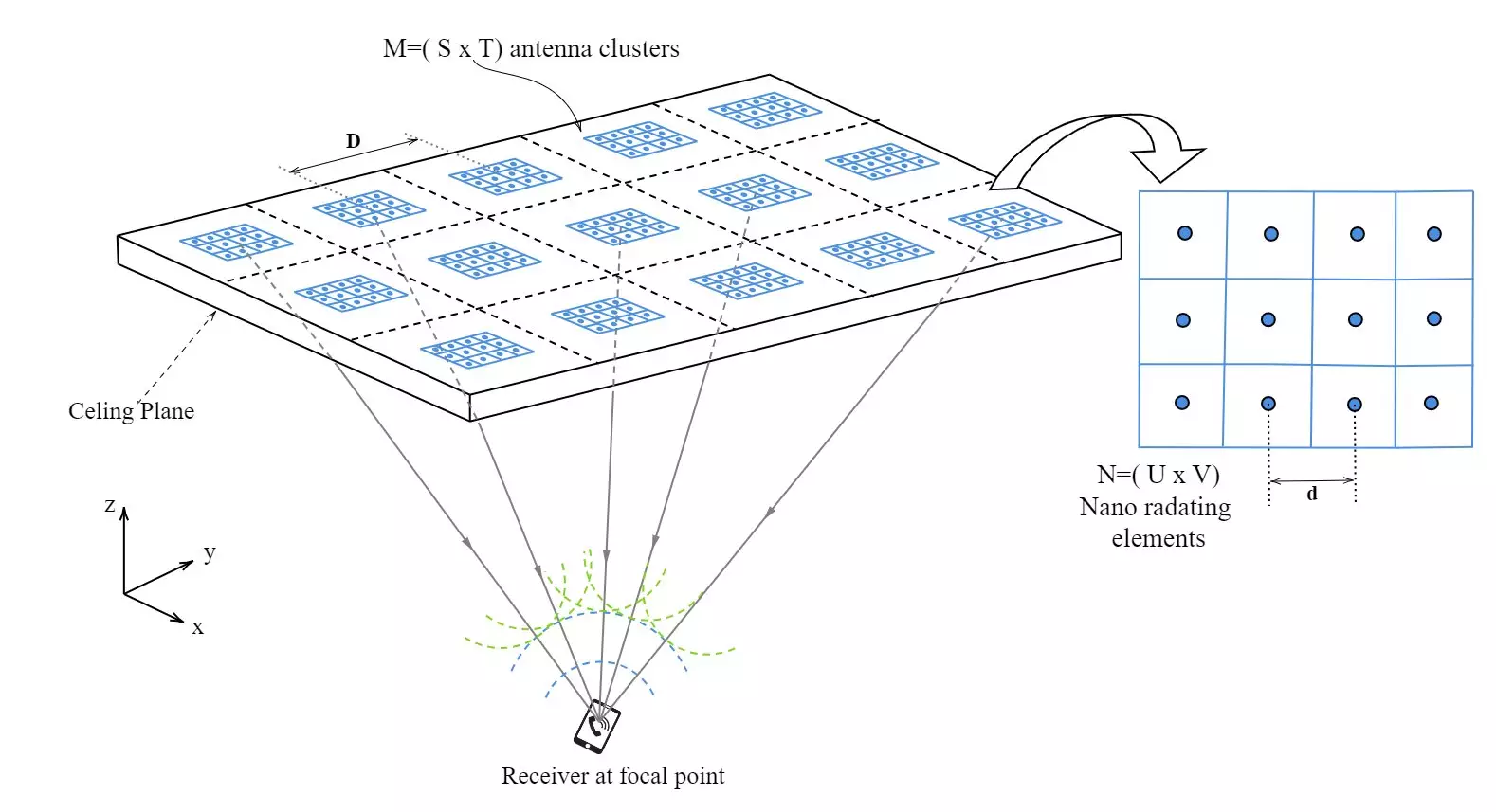
At the forefront of OWC technology is a groundbreaking research initiative detailed in the IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology. Central to this research is the novel implementation of a “phased array within a phased array” system, an innovative concept that draws inspiration from quantum mechanics, particularly the principle of quantum superposition. Just as particles can simultaneously exist in multiple states until measured, this optical system utilizes a sophisticated arrangement of smaller antennas grouped within larger arrays to optimize signal transmission.
This multi-layered design eliminates the reliance on a singular transmitter that is frequently susceptible to interference, such as physical obstructions or competing signals. Instead, it adopts a configuration where multiple transmitting clusters work in unison to maintain clarity and reliability. This redundancy not only bolsters signal strength but also ensures a resilient communication link, capable of functioning effectively in diverse environments.
One of the distinctive features of this OWC system is its dual transmission wavelengths, which enhance both the stability and focus of the transmitted signal. This design ensures superior beam accuracy and reduces the likelihood of signal degradation, even when the distance between transmitter clusters is substantial. Such robust performance is essential in today’s fast-paced digital landscape, where delays can result in significant disruptions.
Moreover, the system incorporates an innovative Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) algorithm, inspired by the behavior of ants in nature. This algorithm ensures that only the necessary clusters are activated during transmission, akin to efficiently managing energy consumption in a building by only illuminating rooms in use. Traditional wireless networks often squander energy by leaving active multiple components during idle periods. Through the selective deactivation of idle clusters, this new system dramatically minimizes energy wastage, lowers operational costs, and contributes to environmental sustainability, aligning with the global shift toward greener technologies.
Expansive Applications for OWC Technology
The implications of this research extend far beyond enhancing data speeds. The versatility of OWC technology opens up new avenues for innovation across various sectors. In healthcare facilities, where secure and uninterrupted communication is paramount, OWC can ensure that sensitive medical data is transmitted reliably. Industrial sectors could benefit from enhanced connectivity in environments laden with physical barriers that typically hamper RF signals.
Importantly, the principles developed through this research are not confined to infrared wavelengths alone. The adaptable nature of this technology allows for potential applications across a spectrum of wavelengths, offering the flexibility to evolve as communication needs change over time.
The evolution of wireless communication is less about merely increasing data speeds and more about redefining the fundamental ways in which we connect and communicate. The introduction of Optical Wireless Communication, powered by layered phased array technology and smart energy management, represents a paradigm shift in this field. As we look ahead, this innovative approach not only promises faster and more efficient connectivity but also sets the stage for a future where wireless communication is more reliable, sustainable, and versatile. In an increasingly interconnected world, these advancements could reshape our digital experiences, enhancing everything from everyday communications to transformative industrial applications.