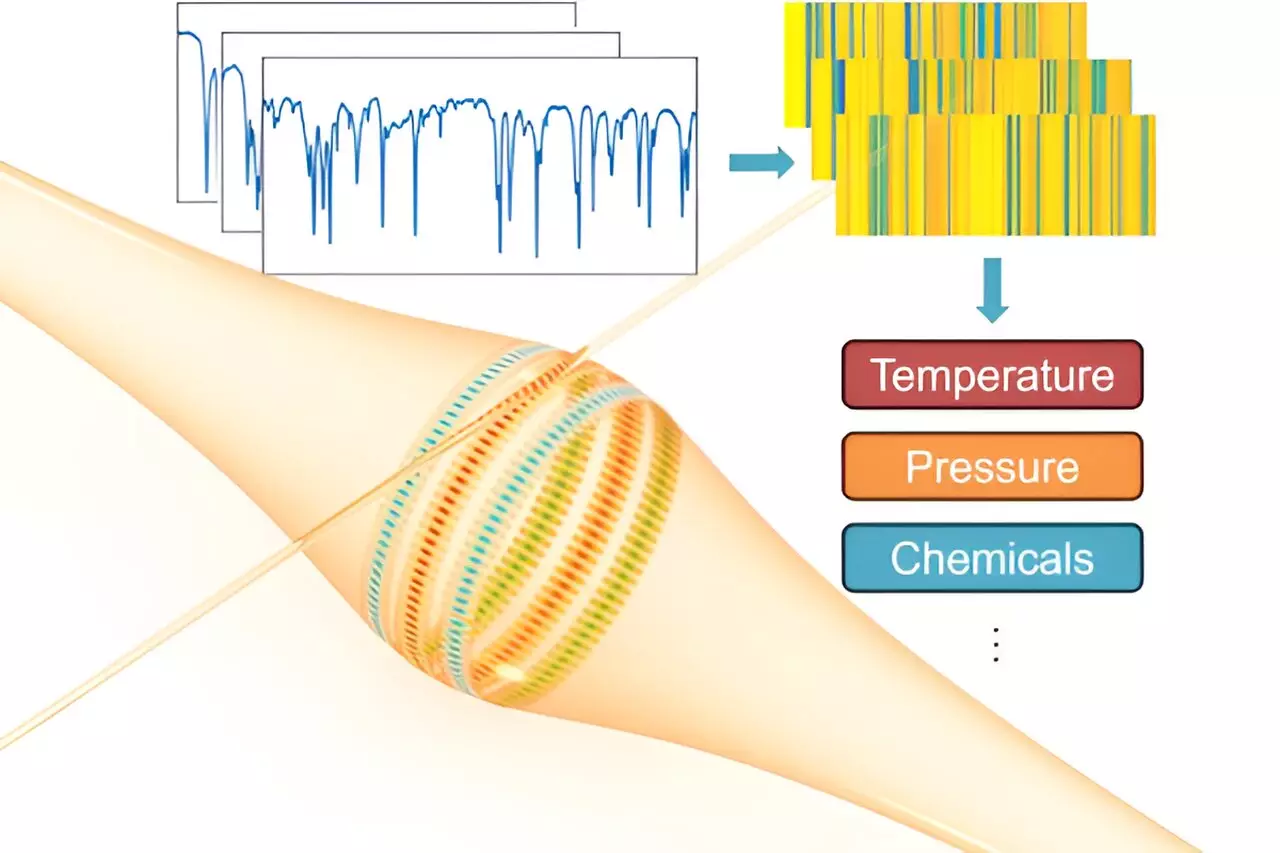
Whispering-gallery-mode (WGM) resonators have long been recognized for their ability to detect and analyze chemical compounds, DNA strands, and even individual molecules with incredible precision. By confining and focusing light in a circular path, WGM microresonators are able to capture and quantify both physical and biochemical characteristics. However, despite their impressive capabilities, the widespread use of WGM resonators has been hindered by their limited dynamic range, resolution, and accuracy.
In a landmark study recently published in the journal IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, researchers Lan Yang and Jie Liao from Washington University in St. Louis unveiled a revolutionary approach to address these limitations. By introducing optical WGM barcodes for multimode sensing, Yang and Liao have pushed the boundaries of traditional WGM technology.
The key innovation in Yang and Liao’s work lies in their ability to monitor multiple resonant modes simultaneously within a single WGM resonator. This novel technique allows for the detection of unique responses from each mode, significantly expanding the range of measurable data. Unlike conventional single-mode sensing, which is constrained by a narrow range of approximately 20 picometers, multimode sensing has the potential to achieve an almost limitless range of measurements.
Commercial Applications and Impact
The implications of multimode WGM sensing technology are vast and wide-ranging. In the realm of biomedical research, this breakthrough could enable researchers to identify subtle changes in molecular interactions with unparalleled sensitivity, leading to advancements in disease diagnosis and drug development. Furthermore, in environmental monitoring, the ability to detect minute variations in temperature, pressure, and pollution levels could revolutionize early warning systems for natural disasters and pollution control efforts.
One of the most promising aspects of multimode sensing is its capacity for continuous monitoring of chemical reactions in real-time. By leveraging the ultrahigh sensitivity of WGM resonators, researchers could gain invaluable insights into chemical processes, with potential applications spanning industries such as pharmaceuticals, materials science, and food production. Multimode sensing opens up a realm of possibilities for exploring the unknown and unlocking the full potential of this groundbreaking technology.
The development of multimode WGM sensing technology represents a significant advancement in the field of optical sensors. By harnessing the power of multiple resonant modes, researchers are now able to achieve greater resolution, accuracy, and sensitivity in their measurements. The commercial applications of this technology are vast, offering promising solutions for complex challenges in various industries. As we continue to push the boundaries of scientific innovation, the future of multimode WGM sensing holds immense promise for transformative advancements in research and development.