Solar energy has become a focal point in the search for sustainable and renewable energy sources. In recent years, researchers have been focusing on improving the efficiency and stability of solar cells, particularly organic solar cells based on perovskite materials. While these organic solar cells have shown promise, there are still challenges to overcome in order to fully exploit their potential.
Organic solar cells based on perovskite materials have demonstrated advantages such as lower fabrication costs, greater flexibility, and tunability compared to traditional silicon-based solar cells. However, the maximum certified power conversion efficiency (PCE) of organic solar cells currently stands at 19.4%, which is lower than that of silicon solar cells. This discrepancy highlights the need for innovative approaches to enhance the efficiency and stability of organic solar cells.
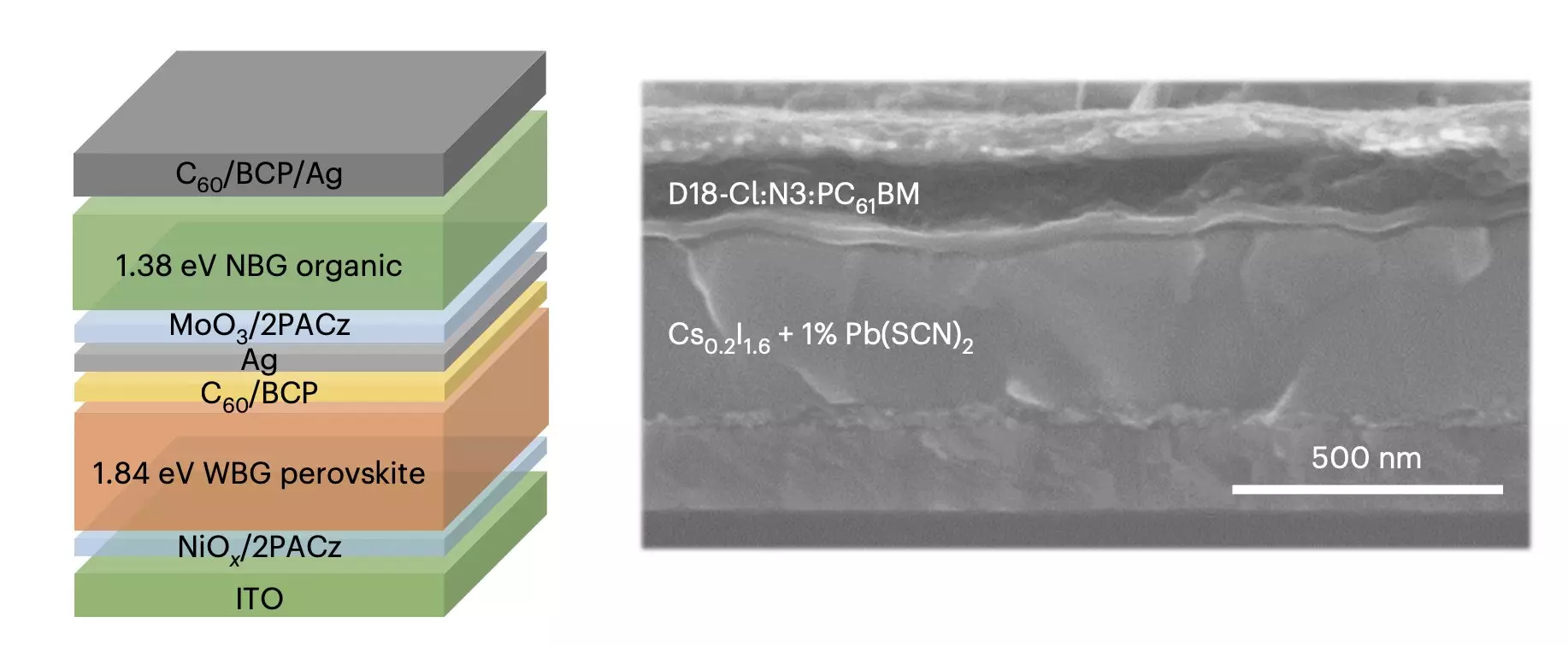
One proposed strategy to improve the efficiency and stability of organic solar cells involves combining them with cells based on mixed halide wide-bandgap perovskites to create perovskite/organic tandem solar cells. While perovskite/organic tandem solar cells hold great potential in achieving high PCEs and stabilities, they are hindered by a phenomenon known as phase segregation. This process degrades the performance of wide-bandgap perovskite cells and impacts the recombination processes at the interconnecting layer of tandem solar cells.
Researchers at Soochow University’s Suzhou Key Laboratory of Novel Semiconductor-optoelectronic materials and devices have made significant strides in addressing phase segregation in wide-bandgap perovskites. Their groundbreaking strategy, as published in Nature Energy, involves incorporating a pseudo-triple-halide alloy in mixed halide perovskites based on iodine and bromine. This innovation aims to suppress phase segregation and enhance the performance and stability of perovskite/organic tandem solar cells.
The introduction of pseudo-halogen thiocyanate ions into iodine/bromide mixed halide perovskites has been shown to prevent halide elements from separating within the solar cells. By slowing down crystallization, the thiocyanate ions hinder ion migration, facilitating the movement of electric charge in the solar cell. This ultimately leads to a reduction in energy loss and the retardation of halide phase segregation during operation.
In initial tests conducted by the researchers, the proposed strategy of incorporating pseudo-halogen thiocyanate ions into wide-bandgap perovskites resulted in perovskite/organic tandem solar cells with impressive performance metrics. The tandem solar cells achieved a PCE of 25.82%, a certified PCE of 25.06%, and operational stability for 1,000 hours. These results demonstrate the efficacy of the strategy in improving the efficiency and stability of perovskite/organic tandem solar cells.
Looking ahead, the methodology introduced by Zhang, Chen, and their collaborators presents promising opportunities for further advancements in the field of solar energy. By applying the strategy to a broader range of wide-bandgap perovskites with varying compositions, researchers could develop next-generation perovskite/organic photovoltaics that are stable, efficient, and long-lasting under different light intensities. The potential impact of this research extends to the wider goal of enhancing the scalability and viability of solar energy as a sustainable power source.
Through innovative strategies and research breakthroughs, the quest for efficient and stable solar cells continues to drive progress in renewable energy technologies. The incorporation of pseudo-halogen thiocyanate ions in wide-bandgap perovskites represents a significant advancement in the development of perovskite/organic tandem solar cells, offering new possibilities for the future of solar energy utilization.